Phosphate availability affects the thylakoid lipid composition and the expression of SQD1, a gene required for sulfolipid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 9465123
- PMCID: PMC19220
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.4.1950
Phosphate availability affects the thylakoid lipid composition and the expression of SQD1, a gene required for sulfolipid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
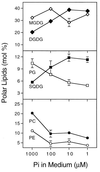
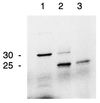
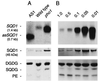
Photosynthetic membranes of higher plants contain specific nonphosphorous lipids like the sulfolipid sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol in addition to the ubiquitous phospholipid phosphatidylglycerol. In bacteria, an environmental factor that drastically affects thylakoid lipid composition appears to be the availability of phosphate. Accordingly, we discovered an increase in the relative amount of sulfolipid and a concomitant decrease in phosphatidylglycerol in Arabidopsis thaliana grown on medium with reduced amounts of phosphate, as well as in the pho1 mutant of A. thaliana deficient in phosphate transport. To investigate the molecular basis of the observed change in lipid composition, we isolated a cDNA of A. thaliana, designated SQD1, that encodes a protein involved in sulfolipid biosynthesis as suggested by three lines of evidence. First, the cDNA shows high sequence similarity to bacterial sqdB genes known to be essential for sulfolipid biosynthesis; second, the SQD1 gene product is imported into chloroplasts where sulfolipid biosynthesis takes place; and third, transgenic plants expressing SQD1 in antisense orientation show a reduction in sulfolipid content. In the pho1 mutant as well as in wild-type plants grown under reduced phosphate availability, increased amounts of SQD1 mRNA and SQD1 protein are detected, suggesting that the increase in sulfolipid content under phosphate limitation is the result of an increased expression of at least one gene required for sulfolipid biosynthesis in A. thaliana. It is suggested that a certain amount of anionic thylakoid lipid is maintained by substituting sulfolipid for phosphatidylglycerol under reduced phosphate availability.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prediction of the active-site structure and NAD(+) binding in SQD1, a protein essential for sulfolipid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999 Sep 1;369(1):30-41. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1344. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999. PMID: 10462438
-
Arabidopsis disrupted in SQD2 encoding sulfolipid synthase is impaired in phosphate-limited growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 16;99(8):5732-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082696499. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11960029 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of a gene essential for sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol biosynthesis in Sinorhizobium meliloti has no detectable effect on root nodule symbiosis.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2000 Jun;13(6):666-72. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.6.666. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2000. PMID: 10830266
-
Biosynthesis and functions of the plant sulfolipid.Prog Lipid Res. 2011 Jul;50(3):234-9. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2011.02.003. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Prog Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21371504 Review.
-
Three enzyme systems for galactoglycerolipid biosynthesis are coordinately regulated in plants.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 28;280(4):2397-400. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R400032200. Epub 2004 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15590685 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteome changes driven by phosphorus deficiency and recovery in the brown tide-forming alga Aureococcus anophagefferens.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28949. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028949. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22194955 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of autophagy by mitochondrial phospholipids in health and diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Jan;1862(1):114-129. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.08.003. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 27502688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does Sulfoquinovosyl Diacylglycerol Synthase OsSQD1 Affect the Composition of Lipids in Rice Phosphate-Deprived Root?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;24(1):114. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010114. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613553 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the plastidic phosphate translocator gene family in Arabidopsis and identification of new phosphate translocator-homologous transporters, classified by their putative substrate-binding site.Plant Physiol. 2003 Mar;131(3):1178-90. doi: 10.1104/pp.016519. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12644669 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-mining for single-copy nuclear markers in ferns.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 8;8(10):e76957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076957. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116189 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

