Assessment of hepatitis B virus DNA stability in serum by the Chiron Quantiplex branched-DNA assay
- PMID: 9466745
- PMCID: PMC104546
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.2.382-386.1998
Assessment of hepatitis B virus DNA stability in serum by the Chiron Quantiplex branched-DNA assay
Abstract
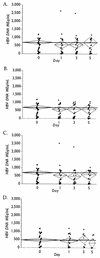
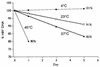
Quantification of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA in serum is used to establish eligibility for treatment and to monitor therapeutic response. With the trend toward centralized testing, defining the conditions that preserve sample integrity is of paramount importance. We therefore evaluated the stability of HBV DNA in 26 previously frozen (PF) and 5 fresh, never previously frozen serum specimens. PF specimens, covering a 3-log10 HBV DNA dynamic range, were thawed and stored at -70, 4, 23, 37, and 45 degrees C (+/-1.5 degrees C) for 0, 24, 72, and 120 h (+/-2 h) and were refrozen at -70 degrees C prior to testing. Five fresh specimens were split into two groups. Both group FG1 and group FG2 specimens were handled as described above; however, group FG1 specimens were subsequently maintained at 4 degrees C and were never frozen prior to testing. Linear regression analysis of PF specimens demonstrated no significant HBV DNA degradation at < or =4 degrees C over 5 days; however, HBV DNA levels decreased by 1.8, 3.4, and 20% per day at 23, 37, and 45 degrees C, respectively. Three independent statistical methods confirmed that the probability of specimen failure, defined as a loss of 20% or more of HBV DNA and/or coagulation of serum, was lowest at < or =4 degrees C and increased with temperature. Because only 10 to 20% of individual patient specimens demonstrated losses of HBV DNA of > or =20% at 23 or 37 degrees C, sufficient numbers of serum specimens must be evaluated to determine overall statistical trends. In conclusion, HBV DNA integrity in separated serum specimens is preserved for at least 5 days when the specimens are stored at -70 or 4 degrees C.
Figures
References
-
- Busch M P, Wilber J C, Johnson P, Tobler L, Evans C S. Impact of specimen handling and storage on detection of hepatitis C virus RNA. Transfusion. 1992;32:420–425. - PubMed
-
- Butterworth L-A, Prior S L, Buda P J, Faoagalo J L, Cooksley W G E. Comparison of four methods for quantitative measurement of hepatitis B viral DNA. J Hepatol. 1996;24:686–691. - PubMed
-
- Davis G L, Lau J Y-N, Urdea M S, Neuwald P D, Wilber J C, Lindsay K, Perrillo R P, Albrecht J. Quantitative detection of hepatitis C virus RNA with a solid-phase signal amplification method: definition of optimal conditions for specimen collection and clinical application in interferon-treated patients. Hepatology. 1994;19:1337–1341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

