4E-BP1, a repressor of mRNA translation, is phosphorylated and inactivated by the Akt(PKB) signaling pathway
- PMID: 9472019
- PMCID: PMC316523
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.4.502
4E-BP1, a repressor of mRNA translation, is phosphorylated and inactivated by the Akt(PKB) signaling pathway
Abstract
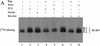
Growth factors and hormones activate protein translation by phosphorylation and inactivation of the translational repressors, the eIF4E-binding proteins (4E-BPs), through a wortmannin- and rapamycin-sensitive signaling pathway. The mechanism by which signals emanating from extracellular signals lead to phosphorylation of 4E-BPs is not well understood. Here we demonstrate that the activity of the serine/threonine kinase Akt/PKB is required in a signaling cascade that leads to phosphorylation and inactivation of 4E-BP1. PI 3-kinase elicits the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 in a wortmannin- and rapamycin-sensitive manner, whereas activated Akt-mediated phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 is wortmannin resistant but rapamycin sensitive. A dominant negative mutant of Akt blocks insulin-mediated phosphorylation of 4E-BP1, indicating that Akt is required for the in vivo phosphorylation of 4E-BP1. Importantly, an activated Akt induces phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 on the same sites that are phosphorylated upon serum stimulation. Similar to what has been observed with serum and growth factors, phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 by Akt inhibits the interaction between 4E-BP1 and eIF-4E. Furthermore, phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 by Akt requires the activity of FRAP/mTOR. FRAP/mTOR may lie downstream of Akt in this signaling cascade. These results demonstrate that the PI 3-kinase-Akt signaling pathway, in concert with FRAP/mTOR, induces the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1.
Figures
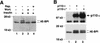
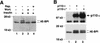
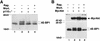


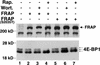
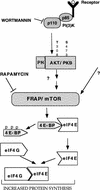
Similar articles
-
Amino acid sufficiency and mTOR regulate p70 S6 kinase and eIF-4E BP1 through a common effector mechanism.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 5;273(23):14484-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.23.14484. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9603962
-
Regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation: a novel two-step mechanism.Genes Dev. 1999 Jun 1;13(11):1422-37. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.11.1422. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 10364159 Free PMC article.
-
Signal pathways involved in activation of p70S6K and phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 following exposure of multiple myeloma tumor cells to interleukin-6.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 3;277(18):15712-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200043200. Epub 2002 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11872747
-
mu-Opioid receptor activates signaling pathways implicated in cell survival and translational control.J Biol Chem. 1998 Sep 4;273(36):23534-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.36.23534. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9722592
-
Modeling resistance to pathway-targeted therapy in ovarian cancer.Cell Cycle. 2005 Aug;4(8):1004-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.8.1869. Epub 2005 Aug 25. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15970711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the translation machinery in cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Apr;14(4):261-78. doi: 10.1038/nrd4505. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 25743081 Review.
-
From Oncogenic Signaling Pathways to Single-Cell Sequencing of Immune Cells: Changing the Landscape of Cancer Immunotherapy.Molecules. 2021 Apr 14;26(8):2278. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082278. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33920054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sinularin Induces Apoptosis through Mitochondria Dysfunction and Inactivation of the pI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway in Gastric Carcinoma Cells.Mar Drugs. 2016 Jul 27;14(8):142. doi: 10.3390/md14080142. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27472346 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting the yeast stress-activated signaling network to inform on stress biology and disease signaling.Curr Genet. 2015 Nov;61(4):503-11. doi: 10.1007/s00294-015-0491-0. Epub 2015 May 10. Curr Genet. 2015. PMID: 25957506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTOR signaling for biological control and cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2013 Aug;228(8):1658-64. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24351. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23460185 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alessi D, James S, Downes CP, Holmes A, Gaffney P, Reese C, Cohen P. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Bα. Curr Biol. 1997;7:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Bellacosa A, Feo DD, Godwin AK, Bell DW, Cheng JQ, Altomare DA, Wan M, Dubeau L, Scambia G, Masciullo V, Ferrandina G, Panici PB, Mancuso S, Neri G, Testa JR. Molecular alterations of the AKT2 oncogene in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Intern J Cancer. 1995;64:280–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
