Potential role of B7-1 and CD28 molecules in immunosuppression in leprosy
- PMID: 9472661
- PMCID: PMC1904849
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00463.x
Potential role of B7-1 and CD28 molecules in immunosuppression in leprosy
Abstract
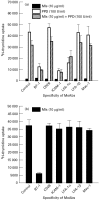
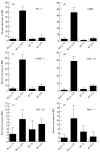
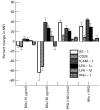
In order to understand the mechanism of unresponsiveness towards Mycobacterium leprae antigens in leprosy, we evaluated the role of M. leprae sonicate antigens in regulating the expression of the costimulatory molecules B7-1, CD28, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), LFA-1alpha, LFA-1beta and Mac-1 on the lymphocytes of both leprosy patients and healthy subjects. It was observed that the expression of B7-1 and CD28 was significantly decreased but the levels of ICAM-1 and LFA-1alpha were increased in patients with untreated borderline leprosy (BL)/lepromatous leprosy (LL) disease. No remarkable change was noticed in the case of borderline tuberculoid (BT) leprosy or treated BL/LL patients. Further, a striking finding was that lymphocytes from healthy subjects cultured with a particularly high dose of M. leprae sonicate antigens down-regulated the expression of B7-1 and CD28 molecules, but up-regulated the display of ICAM-1 and LFA-1alpha. Furthermore, proliferation induced by M. leprae sonicate was inhibited only by anti-B7-1 antibody. Mycobacterium leprae antigen-induced suppression of the proliferation of lymphocytes of healthy volunteers and LL patients was reversed by culturing the lymphocytes with purified protein derivative (PPD). It may be concluded from the findings in this study that down regulation of B7-1 and CD28 in BL/LL leprosy patients may be responsible for a defective T cell signalling by the B7-1/CD28 pathway caused by M. leprae antigens. This may lead to clonal inactivation of M. leprae-reactive T cells, consequently the bacilli grow without restriction in macrophages.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lymphocyte proliferation, IFN-gamma production and limiting dilution analysis of T-cell responses to ICRC and Mycobacterium leprae antigens in leprosy patients.Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1993 Mar;61(1):51-8. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1993. PMID: 8326181
-
Expression of costimulatory molecules (CD80, CD86, CD28, CD152), accessory molecules (TCR alphabeta, TCR gammadelta) and T cell lineage molecules (CD4+, CD8+) in PBMC of leprosy patients using Mycobacterium leprae antigen (MLCWA) with murabutide and T cell peptide of Trat protein.Int Immunopharmacol. 2004 Jan;4(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2003.09.001. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14975355
-
Mycobacterial antigen(s) induce anergy by altering TCR- and TCR/CD28-induced signalling events: insights into T-cell unresponsiveness in leprosy.Mol Immunol. 2010 Feb;47(5):943-52. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.11.009. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20018378
-
HLA and leprosy in the pre and postgenomic eras.Hum Immunol. 2006 Jun;67(6):439-45. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2006.03.009. Epub 2006 Apr 3. Hum Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16728267 Review.
-
CD28/B7 regulation of autoimmune diabetes.Immunol Res. 1997 Feb;16(1):71-84. doi: 10.1007/BF02786324. Immunol Res. 1997. PMID: 9048209 Review.
Cited by
-
Manipulation of costimulatory molecules by intracellular pathogens: veni, vidi, vici!!PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(6):e1002676. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002676. Epub 2012 Jun 14. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22719245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between Central Memory T Cell Expression and Proinflammatory Cytokine Production with Clinical Presentation of Multibacillary Leprosy Relapse.PLoS One. 2015 May 19;10(5):e0127416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127416. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25992795 Free PMC article.
-
ICOS Co-Stimulation: Friend or Foe?Front Immunol. 2016 Aug 10;7:304. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00304. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27559335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterium leprae-host-cell interactions and genetic determinants in leprosy: an overview.Future Microbiol. 2011 Feb;6(2):217-30. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.173. Future Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21366421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD80/CD28 co-stimulation in human brucellosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Dec;146(3):400-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03223.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17100758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boom BR, Mehra V. Immunological unresponsiveness in leprosy. Immunol Rev. 1984;80:5–28. - PubMed
-
- Pancholi P, Mirza A, Bhardwaj N, Steinman RM. Sequestration from immune CD4+ T cells of mycobacterial growing in human macrophages. Science. 1993;260:984–6. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H, Alarcon B, Wileman T, Terhorst C. The T cell receptor/CD3 complex: a dynamic protein ensemble. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:629–31. - PubMed
-
- Damle NK, Klussman K, Linsley PS, Aruffo A. Differential costimulatory effects of adhesion molecules B7, ICAM-1, LFA-3 and VCAM-1 on resting and antigen-primed CD4+T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992;148:1989–92. - PubMed
-
- Springer TA. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990;346:425–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

