CpxP, a stress-combative member of the Cpx regulon
- PMID: 9473036
- PMCID: PMC106961
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.4.831-839.1998
CpxP, a stress-combative member of the Cpx regulon
Abstract
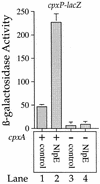
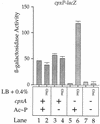
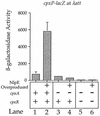
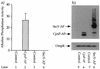
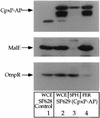
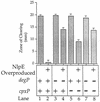
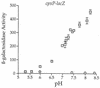
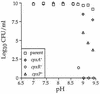
The CpxA/R two-component signal transduction system of Escherichia coli can combat a variety of extracytoplasmic protein-mediated toxicities. The Cpx system performs this function, in part, by increasing the synthesis of the periplasmic protease, DegP. However, other factors are also employed by the Cpx system for this stress-combative function. In an effort to identify these remaining factors, we screened a collection of random lacZ operon fusions for those fusions whose transcription is regulated by CpxA/R. Through this approach, we have identified a new locus, cpxP, whose transcription is stimulated by activation of the Cpx pathway. cpxP specifies a periplasmic protein that can combat the lethal phenotype associated with the synthesis of a toxic envelope protein. In addition, we show that cpxP transcription is strongly induced by alkaline pH in a CpxA-dependent manner and that cpxP and cpx mutant strains display hypersensitivity to growth in alkaline conditions.
Figures


References
-
- Albin R, Weber R, Silverman P M. The Cpx proteins of Escherichia coli K12. Immunologic detection of the chromosomal cpxA gene product. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:4698–4705. - PubMed
-
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique EcoRI sites for selection of EcoRI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978;4:121–136. - PubMed
-
- Cosma C L, Danese P N, Carlson J H, Silhavy T J, Snyder W B. Activation of the Cpx two-component signal transduction pathway in Escherichia coli suppresses envelope associated stresses. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:491–505. - PubMed
-
- Danese P N, Silhavy T J. The ςE and the Cpx signal transduction systems control the synthesis of periplasmic protein-folding enzymes in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1997;11:1183–1193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

