Involvement of outer membrane protein TolC, a possible member of the mar-sox regulon, in maintenance and improvement of organic solvent tolerance of Escherichia coli K-12
- PMID: 9473050
- PMCID: PMC106975
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.4.938-944.1998
Involvement of outer membrane protein TolC, a possible member of the mar-sox regulon, in maintenance and improvement of organic solvent tolerance of Escherichia coli K-12
Abstract
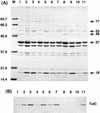
Escherichia coli mutants with improved organic solvent tolerance levels showed high levels of outer membrane protein TolC and inner membrane protein AcrA. The TolC level was regulated positively by MarA, Rob, or SoxS. A possible mar-rob-sox box sequence was found upstream of the tolC gene. These findings suggest that tolC is a member of the mar-sox regulon responsive to stress conditions. When a defective tolC gene was transferred to n-hexane- or cyclohexane-tolerant strains by P1 transduction, the organic solvent tolerance level was lowered dramatically to the decane-tolerant and nonane-sensitive level. The tolerance level was restored by transformation of the transductants with a wild-type tolC gene. Therefore, it is evident that TolC is essential for E. coli to maintain organic solvent tolerance.
Figures


References
-
- Aono R, Aibe K, Inoue A, Horikoshi K. Preparation of organic solvent tolerant mutants from Escherichia coli K-12. Agric Biol Chem. 1991;55:1935–1938.
-
- Aono R, Horikoshi K. Chemical composition of cell walls of alkalophilic strains of Bacillus. J Gen Microbiol. 1983;129:1083–1087.
-
- Aono R, Kobayashi H, Joblin K N, Horikoshi K. Effects of organic solvents on growth of Escherichia coli K-12. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1994;58:2009–2014. - PubMed
-
- Aono R, Kobayashi M, Nakajima H, Kobayashi H. A close correlation between improvement of organic solvent tolerance levels and alteration of resistance toward low levels of multiple antibiotics in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1995;59:213–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

