B lymphocytes differentially use the Rel and nuclear factor kappaB1 (NF-kappaB1) transcription factors to regulate cell cycle progression and apoptosis in quiescent and mitogen-activated cells
- PMID: 9480976
- PMCID: PMC2212175
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.5.663
B lymphocytes differentially use the Rel and nuclear factor kappaB1 (NF-kappaB1) transcription factors to regulate cell cycle progression and apoptosis in quiescent and mitogen-activated cells
Abstract
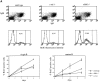
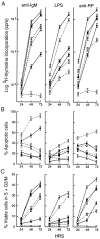
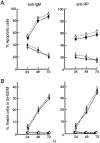
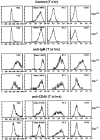
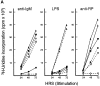
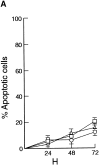
Rel and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB1, two members of the Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factor family, are essential for mitogen-induced B cell proliferation. Using mice with inactivated Rel or NF-kappaB1 genes, we show that these transcription factors differentially regulate cell cycle progression and apoptosis in B lymphocytes. Consistent with an increased rate of mature B cell turnover in naive nfkb1-/- mice, the level of apoptosis in cultures of quiescent nfkb1-/-, but not c-rel-/-, B cells is higher. The failure of c-rel-/- or nfkb1-/- B cells to proliferate in response to particular mitogens coincides with a cell cycle block early in G1 and elevated cell death. Expression of a bcl-2 transgene prevents apoptosis in resting and activated c-rel-/- and nfkb1-/- B cells, but does not overcome the block in cell cycle progression, suggesting that the impaired proliferation is not simply a consequence of apoptosis and that Rel/NF-kappaB proteins regulate cell survival and cell cycle control through independent mechanisms. In contrast to certain B lymphoma cell lines in which mitogen-induced cell death can result from Rel/NF-kappaB-dependent downregulation of c-myc, expression of c-myc is normal in resting and stimulated c-rel-/- B cells, indicating that target gene(s) regulated by Rel that are important for preventing apoptosis may differ in normal and immortalized B cells. Collectively, these results are the first to demonstrate that in normal B cells, NF-kappaB1 regulates survival of cells in G0, whereas mitogenic activation induced by distinct stimuli requires different Rel/NF-kappaB factors to control cell cycle progression and prevent apoptosis.
Figures



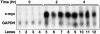
References
-
- Cory S. Regulation of lymphocyte survival by the bcl-2 gene family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:513–543. - PubMed
-
- Clevers HC, Grosschedl R. Transcriptional control of lymphoid development: lessons from gene targeting. Immunol Today. 1996;17:336–343. - PubMed
-
- Kontgen F, Grumont RJ, Strasser A, Metcalf D, Li R, Tarlinton D, Gerondakis S. Mice lacking the c-Rel protooncogene exhibit defects in lymphocyte proliferation, humoral immunity and interleukin-2 expression. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1965–1977. - PubMed
-
- Sha WC, Liou H-C, Toumanen EI, Baltimore D. Targeted disruption of the p50 subunit of NF-κB leads to multifocal defects in the immune system. Cell. 1995;80:321–330. - PubMed
-
- Snapper CM, Zelazowski P, Rosas FR, Kehry MR, Tian M, Baltimore D, Sha WC. B cells from p50/ NF-κB knockout mice have selective defects in proliferation, differentiation, germ-line CH transcription, and Ig class switching. J Immunol. 1996;156:183–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

