Immunization with a lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus peptide mixed with heat shock protein 70 results in protective antiviral immunity and specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- PMID: 9480978
- PMCID: PMC2212166
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.5.685
Immunization with a lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus peptide mixed with heat shock protein 70 results in protective antiviral immunity and specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Abstract
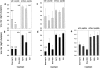
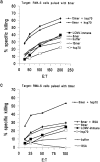
Heat shock proteins (hsp's) isolated from murine cancer cells can elicit protective immunity and specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) by channeling tumor-derived peptides bound to hsp's to the major histocompatibility class I antigen presentation pathway. Here we have investigated if hsp70 can be used in a novel peptide vaccine for the induction of protective antiviral immunity and memory CTLs. A CTL epitope from the well-defined lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) system was mixed with recombinant hsp70 in vitro under conditions that optimize peptide binding to hsp70. Mice were immunized with the hsp70-peptide mixture and challenged with LCMV. Virus titers were reduced 10-100-fold in these mice compared to control mice. Immunization with the hsp70-peptide mixture resulted in the development of CTL memory cells that could be reactivated during LCMV infection, and that in a 51Cr-release assay could lyse cells pulsed with the same peptide, but not cells pulsed with another LCMV peptide. These results show that hsp70 can be used with CTL epitopes to induce efficient protective antiviral immunity and the generation of peptide-specific CTLs. The results also demonstrate the usefulness of hsp70 as an alternative to adjuvants and DNA vectors for the delivery of CTL epitopes to antigen-presenting cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antiviral cytotoxic T-cell memory by vaccination with recombinant Listeria monocytogenes.J Virol. 1996 May;70(5):2902-10. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.5.2902-2910.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8627765 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo induction of a high-avidity, high-frequency cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response is associated with antiviral protective immunity.J Virol. 2000 Jul;74(13):5769-75. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.13.5769-5775.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10846055 Free PMC article.
-
Protective immunity does not correlate with the hierarchy of virus-specific cytotoxic T cell responses to naturally processed peptides.J Exp Med. 1998 May 18;187(10):1647-57. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.10.1647. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9584143 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Db- and Kb-restricted subdominant cytotoxic T-cell responses in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-infected mice.Virology. 1998 Jan 5;240(1):158-67. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8934. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9448700
-
A protective cytotoxic T cell response to a subdominant epitope is influenced by the stability of the MHC class I/peptide complex and the overall spectrum of viral peptides generated within infected cells.Eur J Immunol. 1998 Oct;28(10):3301-11. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199810)28:10<3301::AID-IMMU3301>3.0.CO;2-Q. Eur J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9808199
Cited by
-
The inducible Hsp70 as a marker of tumor immunogenicity.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2001 Apr;6(2):121-5. doi: 10.1379/1466-1268(2001)006<0121:tihaam>2.0.co;2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2001. PMID: 11599573 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-mediated uptake of antigen/heat shock protein complexes results in major histocompatibility complex class I antigen presentation via two distinct processing pathways.J Exp Med. 2000 Jun 5;191(11):1957-64. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.11.1957. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10839810 Free PMC article.
-
The ability of heat-killed Mycobacterium vaccae to stimulate a cytotoxic T-cell response to an unrelated protein is associated with a 65 kilodalton heat-shock protein.Immunology. 2001 Feb;102(2):225-33. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01174.x. Immunology. 2001. PMID: 11260328 Free PMC article.
-
Highly efficient antiviral CD8+ T-cell induction by peptides coupled to the surfaces of liposomes.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009 Oct;16(10):1383-92. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00116-09. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19675224 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock protein-based therapeutic strategies against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection.Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1999;7(1-2):80-90. doi: 10.1155/S1064744999000150. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 10231014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gething M-J, Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992;355:33–45. - PubMed
-
- Hartl F-U, Hlodan R, Langer T. Molecular chaperones in protein folding: the art of avoiding sticky situations. TIBS (Trends Biochem Sci) 1994;19:20–25. - PubMed
-
- Blond-Elguindi S, Cwirla SE, Dower WJ, Lipshutz RJ, Sprang SR, Sambrook JF, Gething MJH. Affinity panning of a library of peptides displayed on bacteriophages reveals the binding specificity of BiP. Cell. 1993;75:717–728. - PubMed
-
- Fourie AM, Sambrook JF, Gething MJH. Common and divergent peptide binding specificities of hsp70 molecular chaperones. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:30470–30478. - PubMed
-
- Craig EA, Weissman JS, Horwich AL. Heat shock proteins and molecular chaperones: mediators of protein conformation and turnover in the cell. Cell. 1994;78:365–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

