Specific T helper cell requirement for optimal induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against major histocompatibility complex class II negative tumors
- PMID: 9480979
- PMCID: PMC2212165
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.5.693
Specific T helper cell requirement for optimal induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against major histocompatibility complex class II negative tumors
Abstract
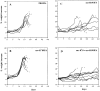
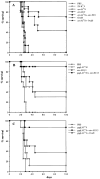
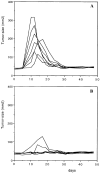
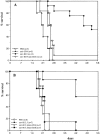
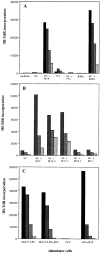
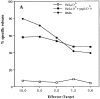
This study shows that induction of tumor-specific CD4+ T cells by vaccination with a specific viral T helper epitope, contained within a synthetic peptide, results in protective immunity against major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II negative, virus-induced tumor cells. Protection was also induced against sarcoma induction by acutely transforming retrovirus. In contrast, no protective immunity was induced by vaccination with an unrelated T helper epitope. By cytokine pattern analysis, the induced CD4+ T cells were of the T helper cell 1 type. The peptide-specific CD4+ T cells did not directly recognize the tumor cells, indicating involvement of cross-priming by tumor-associated antigen-presenting cells. The main effector cells responsible for tumor eradication were identified as CD8+ cytotoxic T cells that were found to recognize a recently described immunodominant viral gag-encoded cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitope, which is unrelated to the viral env-encoded T helper peptide sequence. Simultaneous vaccination with the tumor-specific T helper and CTL epitopes resulted in strong synergistic protection. These results indicate the crucial role of T helper cells for optimal induction of protective immunity against MHC class II negative tumor cells. Protection is dependent on tumor-specific CTLs in this model system and requires cross-priming of tumor antigens by specialized antigen-presenting cells. Thus, tumor-specific T helper epitopes have to be included in the design of epitope-based vaccines.
Figures

References
-
- Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Thakur A, Clements V. Rejection of mouse sarcoma cells after transfection of MHC class II genes. J Immunol. 1990;144:4068–4071. - PubMed
-
- Chen P, Aanathaswamy H. Rejection of K1735 murine melanoma in syngeneic hosts requires expression of MHC class I antigens and either class II antigens or IL-2. J Immunol. 1993;151:244–255. - PubMed
-
- Yoshimura A, Shiku H, Nakayama E. Rejection of an IA+ variant line of FBL-3 leukemia by cytotoxic T lymphocytes with CD4+ and CD4−CD8−T cell receptor-αβ phenotypes generated in CD8-depleted C57BL/6 mice. J Immunol. 1993;150:4900–4910. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg PD. Adoptive T cell therapy of tumors: mechanisms operative in the recognition and elimination of tumor cells. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:281–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

