Recognition of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-E complexed with HLA class I signal sequence-derived peptides by CD94/NKG2 confers protection from natural killer cell-mediated lysis
- PMID: 9480992
- PMCID: PMC2212178
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.5.813
Recognition of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-E complexed with HLA class I signal sequence-derived peptides by CD94/NKG2 confers protection from natural killer cell-mediated lysis
Abstract
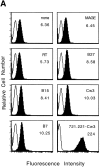
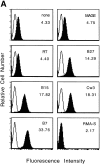
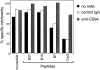
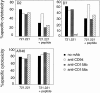
Human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-E is a nonclassical HLA class I molecule, the gene for which is transcribed in most tissues. It has recently been reported that this molecule binds peptides derived from the signal sequence of HLA class I proteins; however, no function for HLA-E has yet been described. We show that natural killer (NK) cells can recognize target cells expressing HLA-E molecules on the cell surface and this interaction results in inhibition of the lytic process. Furthermore, HLA-E recognition is mediated primarily through the CD94/NKG2-A heterodimer, as CD94-specific, but not killer cell inhibitory receptor (KIR)-specific mAbs block HLA-E-mediated protection of target cells. Cell surface HLA-E could be increased by incubation with synthetic peptides corresponding to residues 3-11 from the signal sequences of a number of HLA class I molecules; however, only peptides which contained a Met at position 2 were capable of conferring resistance to NK-mediated lysis, whereas those having Thr at position 2 had no effect. Interestingly, HLA class I molecules previously correlated with CD94/NKG2 recognition all have Met at residue 4 of the signal sequence (position 2 of the HLA-E binding peptide), whereas those which have been reported not to interact with CD94/NKG2 have Thr at this position. Thus, these data show a function for HLA-E and suggest an alternative explanation for the apparent broad reactivity of CD94/NKG2 with HLA class I molecules; that CD94/NKG2 interacts with HLA-E complexed with signal sequence peptides derived from "protective" HLA class I alleles rather than directly interacting with classical HLA class I proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Madden DR. The three-dimensional structure of peptide-MHC complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:587–622. - PubMed
-
- Shawar SM, Vyas JV, Rodgers JR, Rich RR. Antigen presentation by major histocompatibility complex class I-bmolecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:839–880. - PubMed
-
- Lee N, Malacko AR, Ishitani A, Chen MC, Bajorath J, Marquardt H, Geraghty DE. The membrane-bound and soluble forms of HLA-G bind identical sets of peptides but differ with respect to TAP association. Immunity. 1995;3:591–600. - PubMed
-
- Koller BH, Geraghty DE, Shimizu Y, DeMars R, Orr HT. HLA-E: a novel HLA class I gene expressed in resting T-lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988;141:897–904. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

