Submaximal stimulation of porcine endothelial cells causes focal Ca2+ elevation beneath the cell membrane
- PMID: 9481676
- PMCID: PMC2230695
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.109bx.x
Submaximal stimulation of porcine endothelial cells causes focal Ca2+ elevation beneath the cell membrane
Abstract
1. Endothelial cell activation is correlated with increased cytosolic Ca2+ concentration, often monitored with cytoplasmic Ca2+ dyes, such as fura-2 and Calcium Green-1. We tested the hypothesis that during weak stimulation of porcine coronary artery endothelial cells, focal, subplasmalemmal Ca2+ elevations occur which are controlled by cell membrane Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange near mitochondrial membrane and superficial endoplasmic reticulum (SER). 2. Bulk Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]b) was monitored using fura-2 or Calcium Green-1 and subplasmalemmal Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]sp) was determined with FFP-18. The distribution of the SER network was estimated using laser scanning and deconvolution microscopy. 3. Sodium fluoride (10 mmol l-1) and submaximal concentrations of bradykinin (Bk; 1 nmol l-1) stimulated Ca2+ entry with no increase in [Ca2+]b. Although inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation and intracellular Ca2+ release in response to both stimuli were similar, Ca2+ entry in response to NaF exceeded that in response to 1 nmol l-1 BK by fourfold, suggesting additional effects of NaF on Ca+ entry pathways but stimulation via intracellular Ca2+ release. 4. Prevention of Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange activity by decreasing extracellular Na+ unmasked intracellular Ca2+ release in response to NaF and 1 nmol l-1 Bk, indicated by an increase in [Ca2+]b. Thereby, NaF depleted Bk-releasable Ca2+ pools, while mitochondrial Ca2+ content (released with FCCP or oligomycin) and the amount of Ca2+ stored within the cells (released with ionomycin) was increased compared with cells treated with NaF under normal Na+ conditions. The NaF-initiated increase in [Ca2+]b and depletion of Bk-releasable Ca2+ pool(s) in the low-Na+ condition was diminished by 25 mumol l-1 ryanodine, indicating the involvement of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release (CICR). 5. In simultaneous recordings of [Ca2+]sp (with FFP-18) and [Ca2+]b (with Calcium Green-1), 1 nmol l-1 Bk or 10 mmol l-1 NaF yielded focal [Ca2+] elevation in the subplasmalemmal region with no increase in the perinuclear area. 6. Treatment with 10 mumol-1 nocodazole caused the SER to collapse and unmasked Ca2+ release in response to 1 nmol l-1 Bk and 10 mmol l-1 NaF, similar to low-Na+ conditions, while the effect of thapsigargin was not changed. 7. These data show that in endothelial cells, focal, subplasmalemmal Ca2+ elevations in response to small or slow IP3 formation occur due to vectorial Ca2+ release from the SER towards the plasmalemma followed by Ca2+ extrusion by Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange. While these local Ca2+ elevations are not detectable with Ca2+ dyes for the determination of [Ca2+]b, prevention of Ca2+ extrusion or SER disruption yields increases in [Ca2+]b partially due to CICR. 8. All of the data support our hypothesis that in weakly stimulated endothelial cells, intracellular Ca2+ release and [Ca2+] elevation are limited to the subplasmalemmal region. We propose that the SER co-operates with associated parts of the plasma membrane to control Ca2+ homeostasis, Ca2+ distribution and Ca2+ entry. The existence of such a subplasmalemmal Ca2+ control unit (SCCU) needs to be considered in discussions of Ca2+ signalling, especially when cytoplasmic Ca2+ dyes, such as fura-2 or Calcium Green-1, are used.
Figures
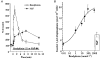





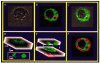

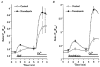


References
-
- Busse R, Mülsch A, Flemming I, Hecker M. Mechanisms of nitric oxide release from the vascular endothelium. Circulation. 1993;87(suppl V):V18–25.
-
- Cabello OA, Schilling WP. Vectorial Ca2+ flux from the extracellular space to the endoplasmic reticulum via a restricted cytoplsamic compartment regulates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-stimulated Ca2+ release from internal stores in vascular endothelial cells. Biochemical Journal. 1993;295:357–366. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Q, Cannell M, Van Breemen C. The superficial buffer barrier in vascular smooth muscle. Canadian The Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 1992;70:509–514. - PubMed
-
- Etter EF, Minta A, Poenie M, Fay FS. Near-membrane [Ca2+] transients resolved using the Ca2+ indicator FFP18. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 1996;93:5368–5373. 10.1073/pnas.93.11.5368. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garzzini E, Guillon G, Chouinard L, Gagnon J-S, Prezeau L, Gallo-Payet N. Dual effects of fluoro-aluminate on activation of calcium influx and inhibition of agonist-induced calcium mobilization in rat glomerulosa cells. Cell Calcium. 1996;19:29–41. 10.1016/S0143-4160(96)90011-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

