Neuromodulatory inputs maintain expression of a lobster motor pattern-generating network in a modulation-dependent state: evidence from long-term decentralization in vitro
- PMID: 9482805
- PMCID: PMC6792931
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-06-02212.1998
Neuromodulatory inputs maintain expression of a lobster motor pattern-generating network in a modulation-dependent state: evidence from long-term decentralization in vitro
Abstract
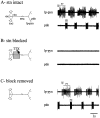
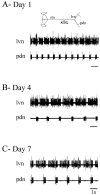
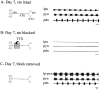
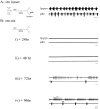
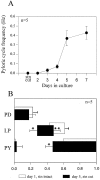
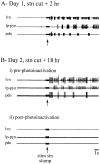
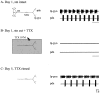
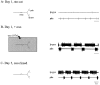
Neuromodulatory inputs play a critical role in governing the expression of rhythmic motor output by the pyloric network in the crustacean stomatogastric ganglion (STG). When these inputs are removed by cutting the primarily afferent stomatogastric nerve (stn) to the STG, pyloric neurons rapidly lose their ability to burst spontaneously, and the network falls silent. By using extracellular motor nerve recordings from long-term organotypic preparations of the stomatogastric nervous system of the lobster Jasus lalandii, we are investigating whether modulatory inputs exert long-term regulatory influences on the pyloric network operation in addition to relatively short-term neuromodulation. When decentralized (stn cut), quiescent STGs are maintained in organ culture, pyloric rhythmicity gradually returns within 3-5 d and is similar to, albeit slower than, the triphasic motor pattern expressed when the stn is intact. This recovery of network activity still occurred after photoinactivation of axotomized input terminals in the isolated STG after migration of Lucifer yellow. The recovery does not depend on action potential generation, because it also occurred in STGs maintained in TTX-containing saline after decentralization. Resumption of rhythmicity was also not activity-dependent, because recovery still occurred in STGs that were chronically depolarized with elevated K+ saline or were maintained continuously active with the muscarinic agonist oxotremorine after decentralization. We conclude that the prolonged absence of extraganglionic modulatory inputs to the pyloric network allows expression of an inherent rhythmogenic capability that is normally maintained in a strictly conditional state when these extrinsic influences are present.
Figures



References
-
- Angelides KJ. Fluorescently labelled Na+ channels are localized and immobilized to synapses of innervated muscle fibres. Nature. 1986;321:63–66. - PubMed
-
- Bal T, Nagy F, Moulins M. The pyloric central pattern generator in crustacea: a set of conditional neuronal oscillators. J Comp Physiol [A] 1988;163:715–727.
-
- Beam KG, Caldwell JH, Campbell DT. Na channels in skeletal muscle concentrated near the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1985;313:588–590. - PubMed
-
- Berdan RC, Easaw JC, Wang R. Alterations in membrane potential after axotomy at different distances from the soma of an identified neuron and the effect of depolarization on neurite outgrowth and calcium channel expression. J Neurophysiol. 1993;69:151–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
