Selective enhancement of P-type calcium currents by isoproterenol in the rat amygdala
- PMID: 9482812
- PMCID: PMC6792919
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-06-02276.1998
Selective enhancement of P-type calcium currents by isoproterenol in the rat amygdala
Abstract
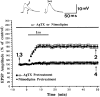
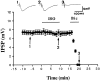
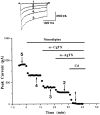
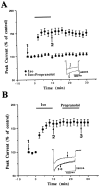
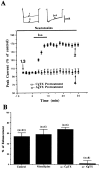
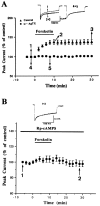
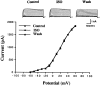
We investigated activation of beta-adrenergic receptor-adenylyl cyclase-cAMP cascade on the whole-cell voltage-dependent Ca2+ currents (ICa) in acutely isolated rat basolateral amygdala neurons. Application of beta-receptor agonist isoproterenol (Iso) caused a long-term enhancement of ICa. The effect of Iso was blocked by concurrent application of beta-receptor antagonist propranolol. However, delayed application of propranolol after the ICa enhancement did not affect Iso-induced potentiation, suggesting that the sustained effect was not caused by a slow washout of Iso. Nimodipine and omega-conotoxin-GVIA reduced the ICa by approximately 35 and approximately 29%, respectively, without reducing enhancement of ICa by Iso significantly. The modulation appeared to involve P-type current, because the enhancement was abolished after pretreatment with omega-agatoxin-IVA. Forskolin, an adenylyl cyclase activator, mimicked the action of Iso in enhancing ICa, and this effect was blocked by an inhibitor of cAMP cascade, indicating a cAMP-dependent mechanism. Iso also induced a long-term potentiation (LTP) of synaptic transmission, which could be prevented by P-type Ca2+ channel blockers. These results suggest that P-type Ca2+ channels were selectively upregulated in the basolateral amygdala neurons, and enhancement of P-type currents could contribute to presynaptic form of LTP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isoproterenol potentiates synaptic transmission primarily by enhancing presynaptic calcium influx via P- and/or Q-type calcium channels in the rat amygdala.J Neurosci. 1996 Feb 1;16(3):1026-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-03-01026.1996. J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8558230 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of voltage-dependent calcium currents by serotonin in acutely isolated rat amygdala neurons.Synapse. 2001 Sep 15;41(4):351-9. doi: 10.1002/syn.1092. Synapse. 2001. PMID: 11494406
-
Dihydropyridine- and neurotoxin-sensitive and -insensitive calcium currents in acutely dissociated neurons of the rat central amygdala.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Feb;77(2):690-701. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.77.2.690. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9065841
-
Alpha2-adrenoreceptor activation inhibits LTP and LTD in the basolateral amygdala: involvement of Gi/o-protein-mediated modulation of Ca2+-channels and inwardly rectifying K+-channels in LTD.Eur J Neurosci. 2003 Apr;17(7):1411-24. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02544.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12713644
-
Cross-modulation of synaptic plasticity by beta-adrenergic and 5-HT1A receptors in the rat basolateral amygdala.J Neurosci. 1999 Jan 15;19(2):570-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-02-00570.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 9880577 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Presynaptic Adrenoceptors.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;285:185-245. doi: 10.1007/164_2024_714. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38755350 Review.
-
GABA(B), opioid and alpha2 receptor inhibition of calcium channels in acutely-dissociated locus coeruleus neurones.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Aug;127(7):1533-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702693. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10455306 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructural characterization of noradrenergic axons and Beta-adrenergic receptors in the lateral nucleus of the amygdala.Front Behav Neurosci. 2010 Oct 13;4:162. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2010.00162. eCollection 2010. Front Behav Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21048893 Free PMC article.
-
Release-independent depression at pyramidal inputs onto specific cell targets: dual recordings in slices of rat cortex.J Physiol. 1999 Aug 15;519 Pt 1(Pt 1):57-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0057o.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10432339 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p/q-Ca2+ channels in metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3-dependent presynaptic long-term depression at nucleus accumbens synapses.J Neurosci. 2002 Jun 1;22(11):4346-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-11-04346.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12040040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aniksztejn L, Ben-Ari Y. Novel form of long-term potentiation produced by a K+ channel blocker in the hippocampus. Nature. 1991;349:67–69. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Blitzer RD, Wong T, Nouranifar R, Lyengar R, Landau EM. Postsynaptic cAMP pathway gates early LTP in hippocampal CA1 region. Neuron. 1995;15:1403–1414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
