Retrotransposon R1Bm endonuclease cleaves the target sequence
- PMID: 9482842
- PMCID: PMC19257
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2083
Retrotransposon R1Bm endonuclease cleaves the target sequence
Abstract
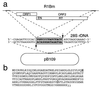
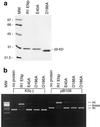
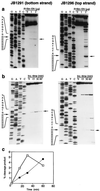
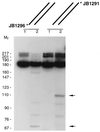
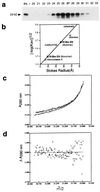
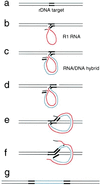
The R1Bm element, found in the silkworm Bombyx mori, is a member of a group of widely distributed retrotransposons that lack long terminal repeats. Some of these elements are highly sequence-specific and others, like the human L1 sequence, are less so. The majority of R1Bm elements are associated with ribosomal DNA (rDNA). R1Bm inserts into 28S rDNA at a specific sequence; after insertion it is flanked by a specific 14-bp target site duplication of the 28S rDNA. The basis for this sequence specificity is unknown. We show that R1Bm encodes an enzyme related to the endonuclease found in the human L1 retrotransposon and also to the apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases. We expressed and purified the enzyme from bacteria and showed that it cleaves in vitro precisely at the positions in rDNA corresponding to the boundaries of the 14-bp target site duplication. We conclude that the function of the retrotransposon endonucleases is to define and cleave target site DNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sequence-specific recognition and cleavage of telomeric repeat (TTAGG)(n) by endonuclease of non-long terminal repeat retrotransposon TRAS1.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jan;21(1):100-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.1.100-108.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11113185 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and phylogenetic analysis of TRAS, telomeric repeat-specific non-LTR retrotransposon families in Lepidopteran insects.Mol Biol Evol. 2001 May;18(5):848-57. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003866. Mol Biol Evol. 2001. PMID: 11319268
-
Functional roles of 3'-terminal structures of template RNA during in vivo retrotransposition of non-LTR retrotransposon, R1Bm.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Apr 6;33(6):1993-2002. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki347. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15814816 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the sequence specificity of the R1Bm endonuclease domain by structural and biochemical studies.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(12):3918-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm397. Epub 2007 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17537809 Free PMC article.
-
Integration, Regulation, and Long-Term Stability of R2 Retrotransposons.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):MDNA3-0011-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0011-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104703 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Entamoeba histolytica LINE/SINE pair inserts at common target sites cleaved by the restriction enzyme-like LINE-encoded endonuclease.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Feb;3(1):170-9. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.1.170-179.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 14871947 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence-specific recognition and cleavage of telomeric repeat (TTAGG)(n) by endonuclease of non-long terminal repeat retrotransposon TRAS1.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jan;21(1):100-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.1.100-108.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11113185 Free PMC article.
-
Completion of LINE integration involves an open '4-way' branched DNA intermediate.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Sep 19;47(16):8708-8719. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz673. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31392993 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary diversity and potential recombinogenic role of integration targets of Non-LTR retrotransposons.Mol Biol Evol. 2005 Oct;22(10):1983-91. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msi188. Epub 2005 Jun 8. Mol Biol Evol. 2005. PMID: 15944437 Free PMC article.
-
Gene silencing triggered by non-LTR retrotransposons in the female germline of Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2003 Jun;164(2):521-31. doi: 10.1093/genetics/164.2.521. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 12807773 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

