Daidzin and its antidipsotropic analogs inhibit serotonin and dopamine metabolism in isolated mitochondria
- PMID: 9482862
- PMCID: PMC19293
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2198
Daidzin and its antidipsotropic analogs inhibit serotonin and dopamine metabolism in isolated mitochondria
Abstract
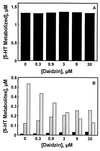
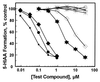
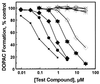
Daidzin, a major active principle of an ancient Chinese herbal treatment (Radix puerariae) for alcohol abuse, selectively suppresses ethanol intake in all rodent models tested. It also inhibits mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH-2). Studies on ethanol intake suppression and ALDH-2 inhibition by structural analogs of daidzin established a link between these two activities and suggested that daidzin may suppress ethanol intake by inhibiting ALDH-2. ALDH-2 is a principal enzyme involved in serotonin (5-HT) and dopamine (DA) metabolism. Thus, daidzin may act by inhibiting 5-HT and DA metabolism. To evaluate this possibility, we have studied the effect of daidzin and its analogs on 5-HT and DA metabolism in isolated hamster and rat liver mitochondria. Daidzin potently inhibits the formation of 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA) and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) from their respective amines in isolated mitochondria. Inhibition is concentration-dependent and is accompanied by a concomitant accumulation of 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetaldehyde and 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde. Daidzin analogs that suppress hamster ethanol intake also inhibit 5-HIAA and DOPAC formation. Comparing their effects on mitochondria-catalyzed 5-HIAA or DOPAC formation and hamster ethanol intake reveals a positive correlation-the stronger the inhibition on 5-HIAA or DOPAC formation, the greater the ethanol intake suppression. Daidzin and its active analogs, at concentrations that significantly inhibit 5-HIAA formation, have little or no effect on mitochondria-catalyzed 5-HT depletion. It appears that the antidipsotropic action of daidzin is not mediated by 5-HT (or DA) but rather by its reactive intermediates 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetaldehyde and, presumably, 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde as well, which accumulates in the presence of daidzin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The mitochondrial monoamine oxidase-aldehyde dehydrogenase pathway: a potential site of action of daidzin.J Med Chem. 2000 Nov 2;43(22):4169-79. doi: 10.1021/jm990614i. J Med Chem. 2000. PMID: 11063613
-
Biogenic aldehyde(s) derived from the action of monoamine oxidase may mediate the antidipsotropic effect of daidzin.Chem Biol Interact. 2001 Jan 30;130-132(1-3):919-30. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(00)00245-3. Chem Biol Interact. 2001. PMID: 11306106
-
Daidzin inhibits mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase and suppresses ethanol intake of Syrian golden hamsters.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Mar 4;94(5):1675-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.5.1675. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9050837 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-dipsotropic isoflavones: the potential therapeutic agents for alcohol dependence.Med Res Rev. 2003 Nov;23(6):669-96. doi: 10.1002/med.10049. Med Res Rev. 2003. PMID: 12939789 Review.
-
Kudzu root: an ancient Chinese source of modern antidipsotropic agents.Phytochemistry. 1998 Feb;47(4):499-506. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(97)00723-1. Phytochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9461670 Review.
Cited by
-
Puerarin ameliorates 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rats: possible neuromodulation and antioxidant mechanisms.Neurochem Res. 2014 Feb;39(2):321-32. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1225-7. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 24346712
-
The aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 polymorphisms on neuropsychological performance in bipolar II disorder with or without comorbid anxiety disorder.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 9;13(2):e0192229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192229. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29425204 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Puerariae Radix Extract on Endotoxin Receptors and TNF-α Expression Induced by Gut-Derived Endotoxin in Chronic Alcoholic Liver Injury.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:234987. doi: 10.1155/2012/234987. Epub 2012 Oct 21. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 23133491 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnopharmacological Applications Targeting Alcohol Abuse: Overview and Outlook.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 14;10:1593. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01593. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32116660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 rs671 variant enhances amyloid β pathology.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 22;15(1):2594. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46899-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38519490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keung W M, Vallee B L. EXS. 1994;71:1254–1260. - PubMed
-
- Heyman G M, Keung W M, Vallee B L. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20:1083–1087. - PubMed
-
- Overstreet D H, Lee Y W, Rezvani A H, Pei Y H, Criswell H E, Janowsky D S. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20:221–227. - PubMed
-
- Overstreet D H, Rezvani A H, Lee Y W. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20:16A. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

