Model studies directed toward the application of boron neutron capture therapy to rheumatoid arthritis: boron delivery by liposomes in rat collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 9482920
- PMCID: PMC19402
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2531
Model studies directed toward the application of boron neutron capture therapy to rheumatoid arthritis: boron delivery by liposomes in rat collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
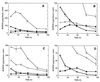
The application of boron neutron capture therapy to rheumatoid arthritis requires the selective delivery of the boron-10 isotope to the synovitic tissue. The use of liposomes as a boron delivery method has been explored through the measurement of the time course biodistribution of boron in rats with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Small unilamellar vesicles were composed of a 1:1 mixture of distearoylphosphatidylcholine and cholesterol, incorporated K[nido-7-CH3(CH2)15-7,8-C2B9H11] as an addend in the lipid bilayer and encapsulated Na3[a2-B20H17NH2CH2CH2NH2] in the aqueous core. The tissue concentration of boron delivered by liposomes was determined by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy after intravenous injection of liposome suspensions into Louvain rats with CIA. With the low injected doses of boron used [13-18 mg of boron per kg (body weight)], the peak boron concentration observed in arthritic synovium was 29 microg of boron per g of tissue. The highest synovium/blood boron ratio observed was 3.0, when the synovial boron concentration was 22 microg of boron per g of tissue. In an attempt to increase the synovium/blood boron ratio by lowering the blood boron concentration, a liposomal formulation characterized by a shorter blood clearance time was examined. Thus, the biodistribution of liposomes with additional K[nido-7-CH3(CH2)15-7, 8-C2B9H11] incorporated in the vesicle membrane not only demonstrated more rapid blood clearance and slightly higher synovium/blood boron ratios but also exhibited reduced boron uptake in synovial tissue. These studies with boron neutron capture therapy for CIA suggest that this form of therapy may be feasible in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selective boron delivery to murine tumors by lipophilic species incorporated in the membranes of unilamellar liposomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1367-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1367. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7877984 Free PMC article.
-
Selectively induced death of macrophages in the synovial lining of murine knee joints using 10B-liposomes and boron neutron capture synovectomy.Int J Radiat Biol. 2009;85(10):860-71. doi: 10.1080/09553000903072454. Int J Radiat Biol. 2009. PMID: 19639504
-
Model studies directed toward the boron neutron-capture therapy of cancer: boron delivery to murine tumors with liposomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9039-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9039. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. PMID: 1409600 Free PMC article.
-
[Minimally invasive cytoselective radiation therapy using boron neutron capture reaction].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Dec;130(12):1687-94. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.1687. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 21139396 Review. Japanese.
-
[Liposomal boron delivery system for neutron capture therapy].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008 Feb;128(2):193-208. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.128.193. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 18239367 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Boron delivery with liposomes for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT): biodistribution studies in an experimental model of oral cancer demonstrating therapeutic potential.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2012 May;51(2):195-204. doi: 10.1007/s00411-011-0399-0. Epub 2012 Jan 21. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22271404
-
Therapeutic efficacy of boron neutron capture therapy mediated by boron-rich liposomes for oral cancer in the hamster cheek pouch model.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Nov 11;111(45):16077-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1410865111. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25349432 Free PMC article.
-
Boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy of cancer.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018 Jun 19;38(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0299-7. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29914561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis By Development of Nanocarriers and their Significance Over Conventional Dosage Forms.Recent Adv Drug Deliv Formul. 2025;19(1):2-15. doi: 10.2174/0126673878324613240805065651. Recent Adv Drug Deliv Formul. 2025. PMID: 40495597 Review.
-
Application of liposomes in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: quo vadis.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014 Feb 4;2014:978351. doi: 10.1155/2014/978351. eCollection 2014. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24688450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harris E D. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1997. p. xix. and 12–13.
-
- Kelley W N, Harris E D, Ruddy S, Sledge C B. Textbook of Rheumatology. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1989. pp. 1934–1953.
-
- Locher G L. Am J Roentogenol Radium Ther. 1936;36:1–13.
-
- Johnson L S, Yanch J C, Shortkroff S, Sledge C B. In: Cancer Neutron Capture Therapy. Mishima Y, editor. New York: Plenum; 1996. pp. 183–188.
-
- Binello E, Shefer R E, Yanch J C. In: Advances in Neutron Capture Therapy. Larsson B, Crawford J, Weinreich R, editors. I. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science; 1997. pp. 459–463.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

