Model studies directed toward the application of boron neutron capture therapy to rheumatoid arthritis: boron delivery by liposomes in rat collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 9482920
- PMCID: PMC19402
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2531
Model studies directed toward the application of boron neutron capture therapy to rheumatoid arthritis: boron delivery by liposomes in rat collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
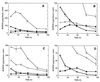
The application of boron neutron capture therapy to rheumatoid arthritis requires the selective delivery of the boron-10 isotope to the synovitic tissue. The use of liposomes as a boron delivery method has been explored through the measurement of the time course biodistribution of boron in rats with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Small unilamellar vesicles were composed of a 1:1 mixture of distearoylphosphatidylcholine and cholesterol, incorporated K[nido-7-CH3(CH2)15-7,8-C2B9H11] as an addend in the lipid bilayer and encapsulated Na3[a2-B20H17NH2CH2CH2NH2] in the aqueous core. The tissue concentration of boron delivered by liposomes was determined by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy after intravenous injection of liposome suspensions into Louvain rats with CIA. With the low injected doses of boron used [13-18 mg of boron per kg (body weight)], the peak boron concentration observed in arthritic synovium was 29 microg of boron per g of tissue. The highest synovium/blood boron ratio observed was 3.0, when the synovial boron concentration was 22 microg of boron per g of tissue. In an attempt to increase the synovium/blood boron ratio by lowering the blood boron concentration, a liposomal formulation characterized by a shorter blood clearance time was examined. Thus, the biodistribution of liposomes with additional K[nido-7-CH3(CH2)15-7, 8-C2B9H11] incorporated in the vesicle membrane not only demonstrated more rapid blood clearance and slightly higher synovium/blood boron ratios but also exhibited reduced boron uptake in synovial tissue. These studies with boron neutron capture therapy for CIA suggest that this form of therapy may be feasible in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Harris E D. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1997. p. xix. and 12–13.
-
- Kelley W N, Harris E D, Ruddy S, Sledge C B. Textbook of Rheumatology. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1989. pp. 1934–1953.
-
- Locher G L. Am J Roentogenol Radium Ther. 1936;36:1–13.
-
- Johnson L S, Yanch J C, Shortkroff S, Sledge C B. In: Cancer Neutron Capture Therapy. Mishima Y, editor. New York: Plenum; 1996. pp. 183–188.
-
- Binello E, Shefer R E, Yanch J C. In: Advances in Neutron Capture Therapy. Larsson B, Crawford J, Weinreich R, editors. I. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science; 1997. pp. 459–463.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

