Hypoalgesia in mice with a targeted deletion of the tachykinin 1 gene
- PMID: 9482938
- PMCID: PMC19441
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2630
Hypoalgesia in mice with a targeted deletion of the tachykinin 1 gene
Abstract
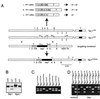
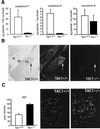
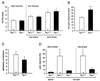
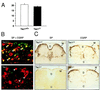
The tachykinin neuropeptides, substance P and substance K, are produced in nociceptive primary sensory neurons and in many brain regions involved in pain signaling. However, the precise role and importance of these neuropeptides in pain responses has been debated. We now show that mice that cannot produce these peptides display no significant pain responses following formalin injection and have an increased pain threshold in the hotplate test. On the other hand, the mutant mice react normally in the tail flick assay and acetic acid-induced writhing tests. These results demonstrate that substance P and/or substance K have essential functions in specific responses to pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deletion of the neuropeptide Y Y1 receptor affects pain sensitivity, neuropeptide transport and expression, and dorsal root ganglion neuron numbers.Neuroscience. 2006 Jun 19;140(1):293-304. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.02.009. Epub 2006 Mar 29. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16564642
-
Functional development of neurokinin peptides substance P and neurokinin A in nociception.Neuroreport. 2003 Aug 26;14(12):1603-7. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200308260-00012. Neuroreport. 2003. PMID: 14502084
-
Diminished anxiety- and depression-related behaviors in mice with selective deletion of the Tac1 gene.J Neurosci. 2002 Nov 15;22(22):10046-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-22-10046.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12427862 Free PMC article.
-
[Biosynthesis of substance P and other mammalian neurokinins].Postepy Biochem. 1992;38(1):23-7. Postepy Biochem. 1992. PMID: 1380701 Review. Polish. No abstract available.
-
Upregulation, release and axonal transport of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in adjuvant inflammation and regulatory function of nerve growth factor.Regul Pept. 1993 Jul 2;46(1-2):150-4. Regul Pept. 1993. PMID: 7692483 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Mouse mast cells and mast cell proteases do not play a significant role in acute tissue injury pain induced by formalin.Mol Pain. 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1744806918808161. doi: 10.1177/1744806918808161. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Mol Pain. 2018. PMID: 30280636 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic Mice for the Translational Study of Neuropathic Pain and Dystonia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8580. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158580. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibromyalgia: Pathogenesis, Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 9;22(8):3891. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083891. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antinociceptive effects of haloperidol and its metabolites in the formalin test in mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Nov;182(4):485-93. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0127-z. Epub 2005 Oct 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 16075285
-
Neurochemical Characterization of the TRPV1-Positive Nociceptive Primary Afferents Innervating Skeletal Muscles in the Rats.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008 Feb;43(2):97-104. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2008.43.2.97. Epub 2008 Feb 20. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008. PMID: 19096612 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

