Enhanced jejunal production of antibodies to Klebsiella and other Enterobacteria in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 9486004
- PMCID: PMC1752411
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.56.7.421
Enhanced jejunal production of antibodies to Klebsiella and other Enterobacteria in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To measure gut immunity directly in jejunal fluid in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Antibodies against three different Enterobacterias were measured in jejunal perfusion fluids (collected by a double balloon perfusion device) of 19 patients with AS, 14 patients with RA, and 22 healthy controls using enzyme linked immunosorbent assay.
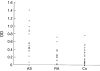
Results: The AS patients had significantly increased jejunal fluid concentrations of IgM, IgG, and IgA class antibodies against Klebsiella pneumoniae, and IgM and IgA class antibodies against Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis compared with healthy controls. When compared with the patients with RA, the AS patients had higher concentrations of IgA and IgG class antibodies only against K pneumoniae. The RA patients had higher IgM class antibody concentrations against all three studied Enterobacterias, when compared with the healthy controls, suggesting an enhanced mucosal immune response in these patients. A three month treatment with sulphasalazine did not decrease enterobacterial antibody concentrations in the 10 patients with AS.
Conclusion: There is strong direct evidence for an abnormal mucosal humoral immune response particularly to K pneumoniae in patients with AS.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

