Th1/Th2 cytokine responses following HIV-1 immunization in seronegative volunteers. The AIDS Vaccine Evaluation Group
- PMID: 9486388
- PMCID: PMC1904920
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00486.x
Th1/Th2 cytokine responses following HIV-1 immunization in seronegative volunteers. The AIDS Vaccine Evaluation Group
Abstract
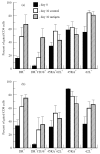
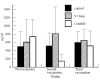
The Th1/Th2 profile that follows human vaccination may profoundly influence the subsequent course of disease after infection. However, the ability to detect IL-4 has been limited outside trials of live vaccination. By using methods in which memory effector cells are allowed to antigenically expand by short term culture, followed by low-dose mitogenic stimulation, we have been able to follow the Th1/Th2 profile in HIV-1 volunteers enrolled in two phase I studies of HIV immunogens (a recombinant gp120 and a multivalent, octomeric V3 loop peptide). Antigen-specific interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) could be detected in primary stimulation, but IL-4 was observed only after antigenic expansion and restimulation. In both of these studies the responses after initial immunizations were dominated by IFN-gamma, with IL-4 appearing only after multiple rounds of immunization, and IL-4 was temporally related to antibody production. Concomitant with the IL-4 production, the amount of supernatant IFN-gamma declined. Antigen-specific IL-10 was not detected in either study. Such techniques, which have been shown to correlate with outcomes in immunotherapy, may prove useful as future surrogates of human vaccine response.
Figures




References
-
- Cease KB, Berzofsky JA. Toward a vaccine for AIDS: the emergence of immunobiology-based vaccine development. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:923–89. - PubMed
-
- Sztein MB, Wasserman SS, Tacket CO, et al. Cytokine production patterns and lymphoproliferative responses in volunteers orally immunized with attenuated vaccine strains of Salmonella typhi. J Infect Dis. 1993;170:1508–17. - PubMed
-
- Ward BJ, Griffin DE. Changes in cytokine production after measles virus vaccination: predominant production of IL-4 suggests induction of a Th2 response. Clinic Immunol Immunopathol. 1993;67:171–7. - PubMed
-
- Romagnani S. Induction of TH1 and Th2 responses: a key role for the ‘natural’ immune response. Immunol Today. 1992;13:379–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

