Induction of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type p55 and p75 in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection
- PMID: 9486392
- PMCID: PMC1904907
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00469.x
Induction of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type p55 and p75 in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection
Abstract
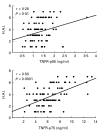
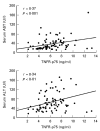
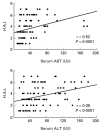
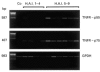
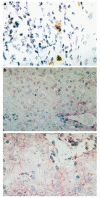
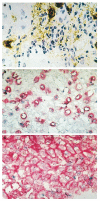
There is evidence that TNF-alpha contributes to the pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatitis. The cellular effects of this cytokine are regulated by two specific receptors, and membranous shedding of these receptors reflects activation of the TNF system. We performed a study of TNF-alpha and functionally active soluble TNF-receptors (TNFR-p55 and -p75) in 105 patients with chronic HCV infection. In HCV RNA-positive patients a significant enhancement of TNF-alpha and both receptor types was observed compared with controls (TNF-alpha 83.8+/-91.7 pg/ml versus 18.8+/-8.4 pg/ml, P<0.001; TNFR-p55 1.4+/-0.4 ng/ml versus 0.9+/-0.2 ng/ml, P<0.0001; TNFR-p75 6.4+/-2.4 ng/ml versus 2.9+/-0.6 ng/ml, P<0.0001, respectively). The enhanced serum levels of TNF-alpha and TNFRs were reflected by a significant expression of TNFR-specific mRNA in peripheral mononuclear cells of HCV-infected patients (P<0.001). Serum aminotransferases correlated with soluble TNFR-p75 (P<0.001) but not with TNFR-p55 and TNF-alpha. We demonstrated an association of the degree of histological inflammation with both TNFRs (P<0.01). Furthermore, enhanced hepatocellular expression of TNF-alpha and TNFRs could be demonstrated by immunohistochemical staining in HCV-infected patients. Sixty-eight out of 105 patients were treated with interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) (3x10(6)U x 3/week). Pretreatment levels of TNF-alpha and TNFRs did not differ between responders and non-responders. Our results demonstrate that TNF-alpha and TNFRs are enhanced in chronic HCV infection and reflect histological activity of the disease. This up-regulation of TNFRs might modify host response and potentially contribute to liver damage in chronic HCV infection.
Figures
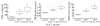
Similar articles
-
Serum levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors and effects of interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection.Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 May;94(5):1332-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01083.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999. PMID: 10235215
-
Shedding of TNF receptors in multiple sclerosis patients.Neurology. 1999 Oct 22;53(7):1409-14. doi: 10.1212/wnl.53.7.1409. Neurology. 1999. PMID: 10534243
-
Dysregulation of membrane-bound tumor necrosis factor-alpha and tumor necrosis factor receptors on mononuclear cells in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection: low percentage of p75-tumor necrosis factor receptor positive cells in patients with advanced disease and high viral load.Blood. 1997 Oct 1;90(7):2670-9. Blood. 1997. PMID: 9326234
-
Divergent roles for p55 and p75 TNF-alpha receptors in the induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1.Am J Pathol. 2003 Mar;162(3):933-41. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63888-6. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12598326 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-alpha in promotion and progression of cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006 Sep;25(3):409-16. doi: 10.1007/s10555-006-9005-3. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006. PMID: 16951987 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety of antitumour necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy in patients with chronic viral infections: hepatitis C, hepatitis B, and HIV infection.Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Nov;63 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii18-ii24. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.028209. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004. PMID: 15479865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of hepatitis B and C co-infection on health-related quality of life in HIV positive individuals.Qual Life Res. 2013 Sep;22(7):1525-35. doi: 10.1007/s11136-012-0283-7. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Qual Life Res. 2013. PMID: 23070749
-
Kinetics of serum soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor (TNF-R) type-I and type-II after a single interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) injection in chronic hepatitis C.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Sep;117(3):556-60. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00992.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10469062 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling and network analysis reveals lipid and steroid metabolism to be the most favored by TNFalpha in HepG2 cells.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 4;5(2):e9063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009063. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20140224 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-induced toxic liver injury results from JNK2-dependent activation of caspase-8 and the mitochondrial death pathway.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 2;281(22):15258-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512953200. Epub 2006 Mar 29. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16571730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alter HJ, Margolis HS, Krawczynski K, et al. The natural history of community acquired hepatitis C in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:1899–905. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Peralta RP, Davis GL, Lau JY. Pathogenetic mechanisms of hepatocellular damage in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 1994;21:255–9. - PubMed
-
- Lau JY, Davis GL, Kniffen J, et al. Significance of serum hepatitis C virus RNA levels in chronic hepatitis C. Lancet. 1993;341:1501–4. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann RM, Diepolder HM, Zachoval R, et al. Mapping of immunodominant CD4+ T lymphocyte epitopes of hepatitis C virus antigens and their relevance during the course of chronic infection. Hepatol. 1995;21:632–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

