Monocytes modulate enhancement of HIV-1 replication by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 9486394
- PMCID: PMC1904906
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00494.x
Monocytes modulate enhancement of HIV-1 replication by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
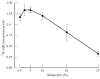
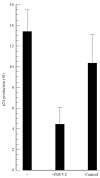
To investigate the effects of Mycobacterium tuberculosis on HIV-1 replication, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG)-vaccinated donors and non-BCG-vaccinated donors were infected in vitro with a lymphotropic isolate of HIV-1 and cultured in the presence of purified protein derivative (PPD). Addition of PPD resulted in enhanced HIV-1 replication and lymphoproliferation in BCG-vaccinated donor PBMC, while PPD had no such effects in control PBMC. HIV-1 replication increased even more when monocytes were removed from PBMC, while lymphoproliferation was decreased. High percentages of monocytes were associated with a decreased HIV-1 replication and proliferation that could not be reversed by addition of antibodies against the cytokines IL-1, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) or indomethacin. PPD stimulates PBMC to release IL-10, a cytokine known to down-regulate proliferation and HIV-1 replication. PPD-induced effects on proliferation as well as HIV-1 replication could be partially blocked by adding a monoclonal antibody against MHC class II molecules, suggesting that part of the mechanism of PPD-induced enhancement is T memory cell activation.
Figures




References
-
- Snider DE, Jr, La Montagne JR. The neglected global tuberculosis problem: a report of the 1992 world congress on tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1994;169:1189–96. - PubMed
-
- Stanley SK, Ostrowski MA, Justement JS, et al. Effect of immunization with common recall antigen on viral expression in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. New Engl J Med. 1996;334:1222–30. - PubMed
-
- Goletti D, Weissman D, Jackson RW, et al. Effect of Mycobacterium tuberculosis on HIV replication. Role of immune activation. J Immunol. 1996;157:1271–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

