Anti-C1q receptor/calreticulin autoantibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- PMID: 9486404
- PMCID: PMC1904908
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00473.x
Anti-C1q receptor/calreticulin autoantibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Abstract
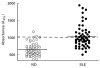
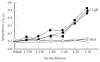
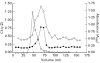
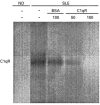
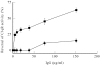
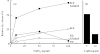
SLE is a disease characterized by the presence of multiple autoantibodies and high levels of circulating immune complexes. We studied the presence and functional relevance of autoantibodies directed against a receptor for the collagen-like stalks of the first subcomponent of complement, also known as calreticulin (cC1qR/CaR), in patients with SLE. In a cross-sectional study it was found that higher titres of antibodies against cC1qR/CaR are present in sera of SLE patients compared with normal donors. No association between anti-cC1qR/CaR titres and SLE disease activity was found. Following gel filtration of SLE serum it was found that anti-cC1qR/CaR reactivity is associated with the peak of monomeric IgG. Purified IgG from patients was able to specifically immunoprecipitate cC1qR/CaR. Since we have shown previously that cC1qR/CaR is able to inhibit the haemolytic activity of Clq, we determined a possible pathogenic role for anti-cC1qR/CaR on complement regulation. IgG derived from SLE serum reversed the inhibitory capacity of cC1qR/CaR in a dose-dependent fashion up to 63%, whereas IgG from normal donors had no significant effect. With respect to the capacity of anti-cC1qR/CaR antibodies to activate neutrophils, it was found that incubation of normal neutrophils with F(ab')2 anti-cC1qR/CaR resulted in a very limited oxidative burst. However, cross-linking of F(ab')2 anti-cC1qR/CaR on the neutrophils clearly induced neutrophil activation. Pre-incubation of the SLE-derived F(ab')2 with cC1qR/CaR prevented activation of neutrophils up to 81+/-5%. These results suggest that the presence of anti-cC1qR/CaR antibodies in patients with SLE may modulate complement and neutrophil activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disease autoantigen-calreticulin can inhibit C1q association with immune complexes.Clin Exp Immunol. 1997 May;108(2):181-90. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1997.3761273.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9158084 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibody to the C3b/C4b receptor and absence of this receptor from erythrocytes of a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus.J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):182-90. doi: 10.1172/JCI111944. J Clin Invest. 1985. PMID: 4019777 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-binding immunoglobulin G in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):902-12. doi: 10.1172/JCI109556. J Clin Invest. 1979. PMID: 479375 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of C1q and the collectins with the potential receptors calreticulin (cC1qR/collectin receptor) and megalin.Immunobiology. 1998 Aug;199(2):208-24. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(98)80028-4. Immunobiology. 1998. PMID: 9777407 Review.
-
Are anti-C1q antibodies different from other SLE autoantibodies?Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010 Aug;6(8):490-3. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.56. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20421881 Review.
Cited by
-
C1q and mannose binding lectin engagement of cell surface calreticulin and CD91 initiates macropinocytosis and uptake of apoptotic cells.J Exp Med. 2001 Sep 17;194(6):781-95. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.6.781. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11560994 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of new autoantibody specificities directed at proteins involved in the transforming growth factor β pathway in patients with systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 May 13;13(3):R74. doi: 10.1186/ar3336. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21569507 Free PMC article.
-
Association of calreticulin expression with disease activity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus patients.Exp Ther Med. 2017 May;13(5):2577-2583. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4235. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28565882 Free PMC article.
-
Calreticulin as a hydrophilic chimeric molecular adjuvant enhances IgG responses to the spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.Microbiol Immunol. 2012 Aug;56(8):554-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2012.00467.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22530918 Free PMC article.
-
A novel autoantibody targeting calreticulin is associated with cancer in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies.Clin Transl Immunology. 2020 Oct 15;9(10):e1195. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1195. eCollection 2020. Clin Transl Immunology. 2020. PMID: 33082955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levinsky RJ, Cameron JS, Soothill JF. Serum immune complexes and disease activity in lupus nephritis. Lancet. 1977;1:564–7. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd W, Schur PH. Immune complexes, complement, and anti-DNA in exacerbations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Med. 1981;60:208–17. - PubMed
-
- Abrass CK, Nies KM, Louie JS, Border WA, Glassock RJ. Correlation and predictive accuracy of circulating immune complexes with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1980;23:273–82. - PubMed
-
- Andre-Schwartz J, Datta SK, Schoenfeld Y, Isenberg DA, Stollar BD, Schwartz RS. Binding of cytoskeletal proteins by monoclonal anti-DNA lupus autoantibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984;31:261–71. - PubMed
-
- Schur PH. Complement in lupus. Clin Rheum Dis. 1975;1:519–43.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

