MP1 encodes an abundant and highly antigenic cell wall mannoprotein in the pathogenic fungus Penicillium marneffei
- PMID: 9488383
- PMCID: PMC108003
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.3.966-973.1998
MP1 encodes an abundant and highly antigenic cell wall mannoprotein in the pathogenic fungus Penicillium marneffei
Abstract
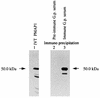
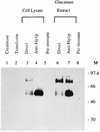
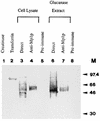
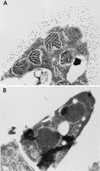
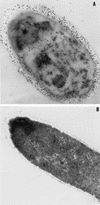
We cloned the MP1 gene, which encodes an abundant antigenic cell wall mannoprotein from the dimorphic pathogenic fungus Penicillium marneffei. MP1 is a unique gene without homologs in sequence databases. It codes for a protein, Mp1p, of 462 amino acid residues, with a few sequence features that are present in several cell wall proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans. It contains two putative N glycosylation sites, a serine- and threonine-rich region for O glycosylation, a signal peptide, and a putative glycosylphosphatidylinositol attachment signal sequence. Specific anti-Mp1p antibody was generated with recombinant Mp1p protein purified from Escherichia coli to allow further characterization of Mp1p. Western blot analysis with anti-Mp1p antibody revealed that Mp1p has predominant bands with molecular masses of 58 and 90 kDa and that it belongs to a group of cell wall proteins that can be readily removed from yeast cell surfaces by glucanase digestion. In addition, Mp1p is an abundant yeast glycoprotein and has high affinity for concanavalin A, a characteristic indicative of a mannoprotein. Furthermore, ultrastructural analysis with immunogold staining indicated that Mp1p is present in the cell walls of the yeast, hyphae, and conidia of P. marneffei. Finally, it was observed that infected patients develop a specific antibody response against Mp1p, suggesting that this protein represents a good cell surface target for host humoral immunity.
Figures


References
-
- Caras I W, Weddell G N. Signal peptide for protein secretion directing glycophospholipid membrane anchor attachment. Science. 1989;243:1196–1198. - PubMed
-
- Cassone A, Conti S, De Bernardis F, Polonelli L. Antibodies, killer toxins and antifungal immunoprotection: a lesson from nature? Immunol Today. 1997;18:164–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

