Functional interference of Sp1 and NF-kappaB through the same DNA binding site
- PMID: 9488441
- PMCID: PMC108839
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1266
Functional interference of Sp1 and NF-kappaB through the same DNA binding site
Abstract
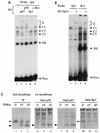
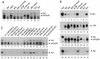
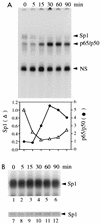
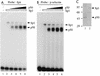
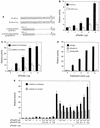
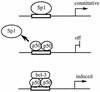
Gene activation by NF-kappaB/Rel transcription factors is modulated by synergistic or antagonistic interactions with other promoter-bound transcription factors. For example, Sp1 sites are often found in NF-kappaB-regulated genes, and Sp1 can activate certain promoters in synergism with NF-kappaB through nonoverlapping binding sites. Here we report that Sp1 acts directly through a subset of NF-kappaB binding sites. The DNA binding affinity of Sp1 to these NF-kappaB sites, as determined by their relative dissociation constants and their relative efficiencies as competitor DNAs or as binding site probes, is in the order of that for a consensus GC box Sp1 site. In contrast, NF-kappaB does not bind to a GC box Sp1 site. Sp1 can activate transcription through immunoglobulin kappa-chain enhancer or P-selectin promoter NF-kappaB sites. p50 homodimers replace Sp1 from the P-selectin promoter by binding site competition and thereby either inhibit basal Sp1-driven expression or, in concert with Bcl-3, stimulate expression. The interaction of Sp1 with NF-kappaB sites thus provides a means to keep an elevated basal expression of NF-kappaB-dependent genes in the absence of activated nuclear NF-kappaB/Rel.
Figures
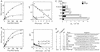
References
-
- Augustin L B, Felsheim R F, Min B H, Fuchs S M, Fuchs J A, Loh H H. Genomic structure of the mouse delta opioid receptor gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;207:111–119. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P A, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Ballard D W, Bohnlein E, Lowenthal J W, Wano Y, Franza B R, Greene W C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the κB element in the IL-2 receptor α gene. Science. 1988;241:1652–1655. - PubMed
-
- Beg A A, Baldwin A S., Jr The IκB proteins: multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1993;7:2064–2070. - PubMed
-
- Beg A A, Sha W C, Bronson R T, Ghosh S, Baltimore D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-κB. Nature. 1995;376:167–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
