ETS-core binding factor: a common composite motif in antigen receptor gene enhancers
- PMID: 9488447
- PMCID: PMC108845
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1322
ETS-core binding factor: a common composite motif in antigen receptor gene enhancers
Abstract
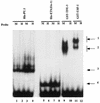
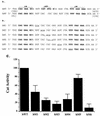
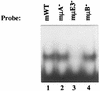
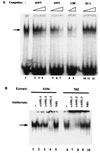
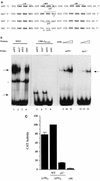
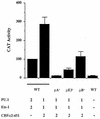
A tripartite domain of the murine immunoglobulin mu heavy-chain enhancer contains the muA and muB elements that bind ETS proteins and the muE3 element that binds leucine zipper-containing basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH-zip) factors. Analysis of the corresponding region of the human mu enhancer revealed high conservation of the muA and muB motifs but a striking absence of the muE3 element. Instead of bHLH-zip proteins, we found that the human enhancer bound core binding factor (CBF) between the muA and mu elements; CBF binding was shown to be a common feature of both murine and human enhancers. Furthermore, mutant enhancers that bound prototypic bHLH-zip proteins but not CBF did not activate transcription in B cells, and conversely, CBF transactivated the murine enhancer in nonlymphoid cells. Taking these data together with the earlier analysis of T-cell-specific enhancers, we propose that ETS-CBF is a common composite element in the regulation of antigen receptor genes. In addition, these studies identify the first B-cell target of CBF, a protein that has been implicated in the development of childhood pre-B-cell leukemias.
Figures



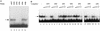
References
-
- Cameron S, Taylor D S, TePas E C, Speck N A, Mathet-Prevot B. Identification of a critical regulatory site in the human interleukin-3 promoter by in vivo footprinting. Blood. 1994;83:2851–2859. - PubMed
-
- Carvajal, I., and R. Sen. Unpublished observations.
-
- Crute B, Lewis A, Wu Z, Bushweller J, Speck N. Biochemical and biophysical properties of the core-binding factor alpha2 (AML1) DNA-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:26251–26260. - PubMed
-
- Ephrussi A, Church G M, Tonegawa S, Gilbert W. B lineage specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985;227:134–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
