Physiological phosphorylation of protein kinase A at Thr-197 is by a protein kinase A kinase
- PMID: 9488457
- PMCID: PMC108855
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1416
Physiological phosphorylation of protein kinase A at Thr-197 is by a protein kinase A kinase
Abstract
Phosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, or protein kinase A, on Thr-197 is required for optimal enzyme activity, and enzyme isolated from either animal sources or bacterial expression strains is found phosphorylated at this site. Autophosphorylation of Thr-197 occurs in Escherichia coli and in vitro but is an inefficient intermolecular reaction catalyzed primarily by active, previously phosphorylated molecules. In contrast, the Thr-197 phosphorylation of newly synthesized protein kinase A in intact S49 mouse lymphoma cells is both efficient and insensitive to activators or inhibitors of intracellular protein kinase A. Using [35S]methionine-labeled, nonphosphorylated, recombinant catalytic subunit as the substrate in a gel mobility shift assay, we have identified an activity in extracts of protein kinase A-deficient S49 cells that phosphorylates catalytic subunit on Thr-197. The protein kinase A kinase activity partially purified by anion-exchange and hydroxylapatite chromatography is an efficient catalyst of protein kinase A phosphorylation in terms of both a low Km for ATP and a rapid time course. Phosphorylation of wild-type catalytic subunit by the kinase kinase activates the subunit for binding to a pseudosubstrate peptide inhibitor of protein kinase A. By both the gel shift assay and a [gamma-32P]ATP incorporation assay, the enzyme is active on wild-type catalytic subunit and on an inactive mutant with Met substituted for Lys-72 but inactive on a mutant with Ala substituted for Thr-197. Combined with the results from mutant subunits, phosphoamino acid analysis suggests that the enzyme is specific for phosphorylation of Thr-197.
Figures
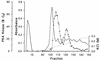
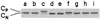
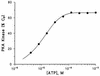
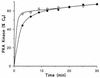

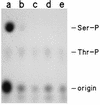

References
-
- Adams J A, McGlone M L, Gibson R, Taylor S S. Phosphorylation modulates catalytic function and regulation in the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1995;34:2447–2454. - PubMed
-
- Bates, F. R., and R. A. Steinberg. Unpublished experiments.
-
- Beebe S J, Øyen O, Sandberg M, Frøysa A, Hansson V, Jahnsen T. Molecular cloning of a tissue specific protein kinase (Cγ) from human testis—representing a third isoform for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1990;4:465–475. - PubMed
-
- Bonner W M, Laskey R A. A film detection method for tritium-labeled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974;46:83–88. - PubMed
-
- Carling D, Aguan K, Woods A, Verhoeven A J M, Beri R K, Brennan C H, Sidebottom C, Davison M D, Scott J. Mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase is homologous to yeast and plant protein kinases involved in the regulation of carbon metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:11442–11448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
