A dominant-negative clathrin mutant differentially affects trafficking of molecules with distinct sorting motifs in the class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) pathway
- PMID: 9490717
- PMCID: PMC2132696
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.140.5.1023
A dominant-negative clathrin mutant differentially affects trafficking of molecules with distinct sorting motifs in the class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) pathway
Abstract
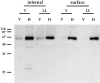
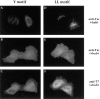
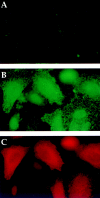
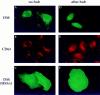
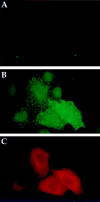
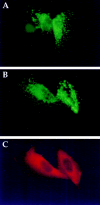
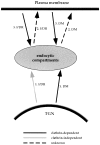
The role of clathrin in intracellular sorting was investigated by expression of a dominant-negative mutant form of clathrin, termed the hub fragment. Hub inhibition of clathrin-mediated membrane transport was established by demonstrating a block of transferrin internalization and an alteration in the intracellular distribution of the cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor. Hubs had no effect on uptake of FITC-dextran, adaptor distribution, organelle integrity in the secretory pathway, or cell surface expression of constitutively secreted molecules. Hub expression blocked lysosomal delivery of chimeric molecules containing either the tyrosine-based sorting signal of H2M or the dileucine-based sorting signal of CD3gamma, confirming a role for clathrin-coated vesicles (CCVs) in recognizing these signals and sorting them to the endocytic pathway. Hub expression was then used to probe the role of CCVs in targeting native molecules bearing these sorting signals in the context of HLA-DM and the invariant chain (I chain) complexed to HLA-DR. The distribution of these molecules was differentially affected. Accumulation of hubs before expression of the DM dimer blocked DM export from the TGN, whereas hubs had no effect on direct targeting of the DR-I chain complex from the TGN to the endocytic pathway. However, concurrent expression of hubs, such that hubs were building to inhibitory concentrations during DM or DR-I chain expression, caused cell surface accumulation of both complexes. These observations suggest that both DM and DR-I chain are directly transported to the endocytic pathway from the TGN, DM in CCVs, and DR-I chain independent of CCVs. Subsequently, both complexes can appear at the cell surface from where they are both internalized by CCVs. Differential packaging in CCVs in the TGN, mediated by tyrosine- and dileucine-based sorting signals, could be a mechanism for functional segregation of DM from DR-I chain until their intended rendezvous in late endocytic compartments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The tyrosine-based lysosomal targeting signal in lamp-1 mediates sorting into Golgi-derived clathrin-coated vesicles.EMBO J. 1996 Oct 1;15(19):5230-9. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8895568 Free PMC article.
-
Endocytic clathrin-coated pit formation is independent of receptor internalization signal levels.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 May;9(5):1177-94. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.5.1177. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9571248 Free PMC article.
-
The biogenesis of the MHC class II compartment in human I-cell disease B lymphoblasts.J Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;132(5):769-85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.5.769. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8603911 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of protein sorting and coat assembly: insights from the clathrin-coated vesicle pathway.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998 Aug;10(4):499-503. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(98)80065-3. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9719871 Review.
-
Protein transport from the secretory to the endocytic pathway in mammalian cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Aug 14;1404(1-2):195-209. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(98)00057-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9714803 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Clathrin and Dynamin in Clathrin Mediated Endocytosis/Synaptic Vesicle Recycling and Implications in Neurological Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jan 18;15:754110. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.754110. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35115907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamin photoinactivation blocks Clathrin and α-adaptin recruitment and induces bulk membrane retrieval.J Cell Biol. 2014 Mar 31;204(7):1141-56. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201310090. Epub 2014 Mar 24. J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24662566 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of clathrin and AP-2 in the trafficking of MHC class II molecules to antigen-processing compartments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 31;102(22):7910-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502206102. Epub 2005 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15911768 Free PMC article.
-
Taming the Triskelion: Bacterial Manipulation of Clathrin.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2019 Feb 27;83(2):e00058-18. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00058-18. Print 2019 May 15. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30814130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocytosis regulates cell soma translocation and the distribution of adhesion proteins in migrating neurons.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 22;6(3):e17802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017802. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21445347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amigorena S, Drake JR, Webster P, Mellman I. Transient accumulation of new class II MHC molecules in a novel endocytic compartment in B lymphocytes. Nature. 1994;369:113–120. - PubMed
-
- Bakke O, Dobberstein B. MHC class II-associated invariant chain contains a sorting signal for endosomal compartments. Cell. 1990;63:707–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

