Mutant Rab7 causes the accumulation of cathepsin D and cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor in an early endocytic compartment
- PMID: 9490721
- PMCID: PMC2132709
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.140.5.1075
Mutant Rab7 causes the accumulation of cathepsin D and cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor in an early endocytic compartment
Abstract
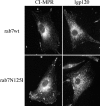
Stable BHK cell lines inducibly expressing wild-type or dominant negative mutant forms of the rab7 GTPase were isolated and used to analyze the role of a rab7-regulated pathway in lysosome biogenesis. Expression of mutant rab7N125I protein induced a dramatic redistribution of cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor (CI-MPR) from its normal perinuclear localization to large peripheral endosomes. Under these circumstances approximately 50% of the total receptor and several lysosomal hydrolases cofractionated with light membranes containing early endosome and Golgi markers. Late endosomes and lysosomes were contained exclusively in well-separated, denser gradient fractions. Newly synthesized CI-MPR and cathepsin D were shown to traverse through an early endocytic compartment, and functional rab7 was crucial for delivery to later compartments. This observation was evidenced by the fact that 2 h after synthesis, both markers were more prevalent in fractions containing light membranes. In addition, both were sensitive to HRP-DAB- mediated cross-linking of early endosomal proteins, and the late endosomal processing of cathepsin D was impaired. Using similar criteria, the lysosomal membrane glycoprotein 120 was not found accumulated in an early endocytic compartment. The data are indicative of a post-Golgi divergence in the routes followed by different lysosome-directed molecules.
Figures


















References
-
- Bleekemolen JE, Stein M, von Figura K, Slot JW, Geuze HJ. The two mannose 6-phosphate receptors have almost identical subcellular distributions in U937 monocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988;47:366–372. - PubMed
-
- Bomsel M, Parton R, Kuznetsov SA, Schroer TA, Gruenberg J. Microtubule- and motor-dependent fusion in vitro between apical and basolateral endocytic vesicles from MDCK cells. Cell. 1990;62:719–731. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino JS, Marks MS, Ohno H, Kirchhausen T. Mechanisms of signal-mediated protein sorting in the endocytic and secretory pathways. Proc Assoc Am Phys. 1996;108:285–295. - PubMed
-
- Borden LA, Einstein R, Gabel CA, Maxfield FR. Acidification-dependent dissociation of endocytosed insulin precedes that of endocytosed proteins bearing the mannose 6-phosphate recognition marker. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:8497–8504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

