Purification of the Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase from Radish Seedlings by Calmodulin-Agarose Affinity Chromatography
- PMID: 9490776
- PMCID: PMC35144
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.116.2.845
Purification of the Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase from Radish Seedlings by Calmodulin-Agarose Affinity Chromatography
Abstract
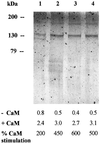
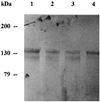
The Ca2+-ATPase of the plasma membrane (PM) of germinating radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seeds was purified by calmodulin (CaM)-affinity chromatography using a batch procedure. PM purified by aqueous two-phase partitioning was solubilized with n-dodecyl beta-d-maltoside and applied to a CaM-agarose matrix. After various washings with decreasing Ca2+ concentrations, the Ca2+-ATPase was eluted with 5 mm ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA). The EDTA-eluted fraction contained about 25% of the loaded Ca2+-ATPase activity, with a specific activity 70-fold higher than that of the starting PM fraction. The EDTA-eluted fraction was highly enriched in a 133-kD polypeptide, which was identified as the PM Ca2+-ATPase by 125I-CaM overlay and fluorescein-isothiocyanate labeling. The PM Ca2+-ATPase cross-reacted with an antiserum against a putative Ca2+-ATPase of the Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplast envelope.
Figures

References
-
- Askerlund P, Evans DE. Plant Physiol Biochem. 1993;31:787–791.
-
- Askerlund P, Sommarin M (1996) Calcium efflux tranporters in higher plants. In M Smallwood, JP Knox, DJ Bowles, eds, Membranes: Specialized Functions in Plants. BIOS Scientific Publishers Ltd., Oxford, UK, pp 281–299
-
- Briars SA, Kessler F, Evans DE. The calmodulin-stimulated ATPase of maize coleoptiles is a 140000-Mr polypeptide. Planta. 1988;176:283–285. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

