The effect of length on the relationship between tension and intracellular [Ca2+] in intact frog skeletal muscle fibres
- PMID: 9490836
- PMCID: PMC2230874
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.179br.x
The effect of length on the relationship between tension and intracellular [Ca2+] in intact frog skeletal muscle fibres
Abstract
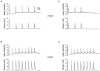
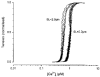
1. The relationship between tension and intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) in intact frog skeletal muscle fibres was determined at two fibre lengths, corresponding to mean sarcomere lengths (SL) of 2.2 and 2.9 micron. Tension and [Ca2+]i were recorded during the slow decline of tension following stimulation in the presence of cyclopiazonic acid (CPA), a sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-uptake pump inhibitor. [Ca2+]i was estimated by injecting the K+ salt form of the fluorescent dye fura-2 into the fibres. Experimental temperature was 3.0 C. 2. At a SL of 2.2 micron, where thick and thin filaments fully overlap, the [Ca2+]i corresponding to 50 % tension generation ([Ca2+]50) was 1.09 +/- 0.02 microM (mean +/- S.E.M., n = 61 contractions). At a SL of 2.9 micron, where overlap is approximately 50 %, the [Ca2+]50 was significantly lower, 0.69 +/- 0. 02 microM (n = 22 contractions). This is in agreement with previous results from skinned fibres. 3. The relationship between tension and [Ca2+]i was very steep, as reported previously from experiments at a SL of 2.2 micron in which the membrane permeant acetoxymethyl ester form of fura-2 was used. The fall in tension from 90 to 10 % occurred in 0.12 +/- 0.01 pCa units (mean +/- S.E.M., n = 61) for a SL of 2.2 micron and 0.17 +/- 0.01 pCa units (n = 22) for a SL of 2.9 micron, corresponding to Hill coefficients of 15.4 and 10.9, respectively. 4. We conclude that the increase in sensitivity of tension to [Ca2+] that occurs in skinned skeletal muscle fibres upon stretch also occurs in intact fibres, that the steepness of the relation between tension and [Ca2+]i in intact fibres reported previously cannot be attributed to the use of the acetoxymethyl ester form of fura-2 to report [Ca2+]i, and that the steepness decreases as myofilament overlap decreases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between tension and slowly varying intracellular calcium concentration in intact frog skeletal muscle.J Physiol. 1997 Apr 1;500 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):177-92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp022008. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9097942 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcomere length dependence of the rate of tension redevelopment and submaximal tension in rat and rabbit skinned skeletal muscle fibres.J Physiol. 1997 Jun 15;501 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):607-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.607bm.x. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9218220 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of rapid shortening on rate of force regeneration and myoplasmic [Ca2+] in intact frog skeletal muscle fibres.J Physiol. 1998 Aug 15;511 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):171-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.171bi.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9679172 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcomere mechanics in uniform and non-uniform cardiac muscle: a link between pump function and arrhythmias.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2008 Jun-Jul;97(2-3):312-31. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2008.02.013. Epub 2008 Feb 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18394686 Review.
-
"Current" advances in mechanically skinned skeletal muscle fibres.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001 Aug;28(8):668-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2001.03502.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11473535 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in Muscle Shear Modulus and Urinary Titin N-Terminal Fragment after Eccentric Exercise.J Sports Sci Med. 2022 Dec 1;21(4):536-544. doi: 10.52082/jssm.2022.536. eCollection 2022 Dec. J Sports Sci Med. 2022. PMID: 36523897 Free PMC article.
-
Length-dependent effects of osmotic compression on skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2000 May;21(4):313-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1005679215704. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2000. PMID: 11032342
-
Potentiation in mouse lumbrical muscle without myosin light chain phosphorylation: is resting calcium responsible?J Gen Physiol. 2013 Mar;141(3):297-308. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201210918. Epub 2013 Feb 11. J Gen Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23401574 Free PMC article.
-
Using Shear-Wave Elastography to Assess Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 6;22(19):7574. doi: 10.3390/s22197574. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36236672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Force-velocity and unloaded shortening velocity during graded potassium contractures in frog skeletal muscle fibres.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2000 Jan;21(1):9-19. doi: 10.1023/a:1005651324472. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2000. PMID: 10813631
References
-
- Claflin DR, Vandenboom R, Morgan DL, Julian FJ. The duration of the intracellular Ca2+ transient increases with increased sarcomere length in intact frog skeletal muscle. Biophysical Journal. 1997;72:A274.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

