Spatio-temporal receptive fields in carp retinal horizontal cells
- PMID: 9490843
- PMCID: PMC2230855
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.223br.x
Spatio-temporal receptive fields in carp retinal horizontal cells
Abstract
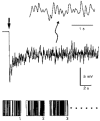
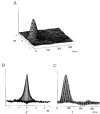
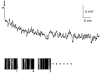
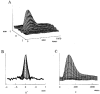
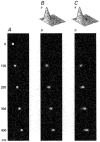
1. The dynamics of the receptive fields of retinal horizontal cells were examined by applying a spatio-temporal modulated light signal to the retina. 2. The spatio-temporal receptive fields of both cone- and rod-driven horizontal cells, estimated through cross-correlation between the modulated light signal and the cells' responses, showed their receptive fields (the space-dependent component) to be reduced in size with time. 3. In cone-driven horizontal cells, the reduction in receptive field size was initially small but then rapidly became prominent with time. The time to peak of the time-dependent component of spatio-temporal receptive fields did not depend on the distance from the centre. 4. Application of a small amount of Co2+, an agent blocking the cone-driven horizontal cells' feedback action on cones, or GABA, resulted in a reversal of the time-dependent shrinkage of receptive fields to time-dependent expansion. 5. In rod-driven horizontal cells, the receptive field shrinkage was slow. The time to peak of the time-dependent component decreased with the distance from the centre. 6. Image processing experiments examining the response pattern in the horizontal cell layer (neural image) to a moving square of light showed smudging of the neural image when the time-dependent receptive field expansion was present, while there was essentially no smudging under conditions of receptive field shrinkage.
Figures



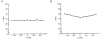
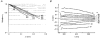
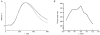
Similar articles
-
Rod and cone contributions to horizontal cell light responses in the mouse retina.J Neurosci. 2008 Jul 2;28(27):6818-25. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1564-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18596157 Free PMC article.
-
[The selective suppression of GABA on cone-driven horizontal cells in carp retina].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 1997 Dec;49(6):639-43. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 1997. PMID: 9863185 Chinese.
-
Kinetics of synaptic transfer from rods and cones to horizontal cells in the salamander retina.Neuroscience. 2003;122(3):785-98. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.08.012. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 14622921
-
Molecular mechanisms characterizing cone photoresponses.Photochem Photobiol. 2007 Jan-Feb;83(1):19-26. doi: 10.1562/2006-02-28-IR-823. Photochem Photobiol. 2007. PMID: 16706600 Review.
-
Rod and cone photoreceptors: molecular basis of the difference in their physiology.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2008 Aug;150(4):369-77. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.04.600. Epub 2008 Apr 26. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18514002 Review.
References
-
- Baldridge WH, Ball AK. Background illumination reduces horizontal cells receptive field size in both normal and 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned goldfish retinas. Visual Neuroscience. 1991;7:441–450. - PubMed
-
- Byzov AL, Shura-Bura TM. Spread of potentials along the network of horizontal cells in the retina of the turtle. Vision Research. 1983;23:389–397. - PubMed
-
- Byzov AL, Trifonov, Yu A, Chailahian LM, Golubtzov KW. Amplification of graded potentials in horizontal cells of the retina. Vision Research. 1977;17:265–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

