Massive expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells during an acute virus infection
- PMID: 9491998
- PMCID: PMC2776648
- DOI: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80469-0
Massive expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells during an acute virus infection
Abstract
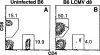
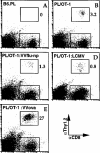
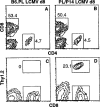
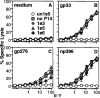
During LCMV infection, CD8+ T cells expand greatly. Bystander activation has been thought to play a role because few cells score as LCMV specific in limiting dilution analysis. In contrast, we find that at least a quarter of the CD8+ cells secrete IFNgamma specifically in response to LCMV peptides at the peak of the response. Moreover, by analyzing the expansion of adoptively transferred LCMV-specific, TCR-transgenic CD8+ T cells in congenic hosts, we have determined that most of the CD8+ cell expansion is virus specific. Analysis of the effect of the monospecific TCR-transgenic T cells on the host response to three LCMV epitopes suggests that CTL precursors compete for sites on the APC in an epitope-specific fashion and that this competition determines the specificity of the response.
Figures


References
-
- Andersson EC, Christensen JP, Scheynius A, Marker O, Thomsen AR. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection is associated with long-standing perturbation of LFA-1 expression on CD8+ T cells. Scand J Immunol. 1995;42:110–118. - PubMed
-
- Bacik I, Cox JH, Anderson R, Yewdell JW, Bennink JR. TAP (transporter associated with antigen processing)-independent presentation of endogenously synthesized peptides is enhanced by endoplasmic reticulum insertion sequences located at the amino- but not carboxyl-terminus of the peptide. J Immunol. 1994;152:381–387. - PubMed
-
- Beverley PCL. Generation of T-cell memory. Current Opinion in Immunology. 1996;8:327–330. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

