CD40 ligand and appropriate cytokines induce switching to IgG, IgA, and IgE and coordinated germinal center and plasmacytoid phenotypic differentiation in a human monoclonal IgM+IgD+ B cell line
- PMID: 9498752
- PMCID: PMC4624333
CD40 ligand and appropriate cytokines induce switching to IgG, IgA, and IgE and coordinated germinal center and plasmacytoid phenotypic differentiation in a human monoclonal IgM+IgD+ B cell line
Abstract
B lymphocytes are induced to undergo Ig class switching and a complex phenotypic differentiation by the milieu of the germinal center. Partly as a result of the lack of a suitable in vitro B cell model, the relationship between these processes in the humans has never been formally established in vitro. We have identified a human monoclonal B cell line, CL-01, that expresses surface IgM and IgD and, upon induction with CD40 ligand, IL-4, and IL-10, switches to all seven downstream isotypes, showing typical DNA switch recombination preceded by germline transcription of targeted CH regions. In CL-01 cells, switch-inducing stimuli trigger concomitant changes in expression of surface IgD, CD23, CD38, and CD77 that parallel those reported in ex vivo isolated tonsillar centroblasts, centrocytes, and memory B cells. Eventually, in the presence of IL-6, CL-01 cells express CD56 and accumulate cytoplasmic IgG and IgA, both traits of plasmacytoid differentiation. Analysis of transcription and recombination of the Ig H locus in sorted CL-01 cells suggest that Ig class switching begins in centroblasts, it extends to all isotypes in centrocytes, and it is extinct in memory B cells. Thus, we have induced coordinated Ig class switching, progression through germinal center phenotypic stages, and differentiation to memory B cells and plasma cells at the level of a single B clonotype. Our data suggest that these processes are likely regulated by a common maturation program, the activation of which may require CD40 ligand, IL-4, IL-10, and IL-6 only.
Figures

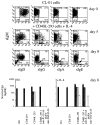
 ), IgA (▨), and IgE (□) accumulated in the fluids of CL-01 cells incubated for 8 days with or without IL-4, and cultured alone, with CD8-293 cells, with CD40L-293 cells, and with CD40L-293 cells in the presence of neutralizing anti-IL-10 and/or anti-TGF-β Abs (the concentrations of IgM and IgE were from cultures with both anti-IL-10 and anti-TGF-β Abs, whereas the concentrations of IgG and IgA were from cultures with anti-IL-10 and anti-TGF-β Abs, respectively). Values are mean ± SD of four determinations from three independent experiments.
), IgA (▨), and IgE (□) accumulated in the fluids of CL-01 cells incubated for 8 days with or without IL-4, and cultured alone, with CD8-293 cells, with CD40L-293 cells, and with CD40L-293 cells in the presence of neutralizing anti-IL-10 and/or anti-TGF-β Abs (the concentrations of IgM and IgE were from cultures with both anti-IL-10 and anti-TGF-β Abs, whereas the concentrations of IgG and IgA were from cultures with anti-IL-10 and anti-TGF-β Abs, respectively). Values are mean ± SD of four determinations from three independent experiments.
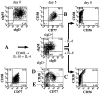
 and lines), JH, 5′S, 3′S, and σ probes (■), and restriction sites. The expected sizes of restriction fragments detected by each switch probe are also indicated. The asterisk indicates a SphI site that is present in the 3′ end of the Sα2 locus, but not in the Sα1 locus. B, Genomic DNA from placenta (upper gel) and unstimulated CL-01 cells (bottom gel) was digested with BglII, HindIII, and SphI restriction enzymes; subjected to electrophoresis on a 0.7% agarose gel; blotted; and probed sequentially with the various σμ, Sμ, σδ, Sγ, Sα, and Sε region probes (shown above each lane).
and lines), JH, 5′S, 3′S, and σ probes (■), and restriction sites. The expected sizes of restriction fragments detected by each switch probe are also indicated. The asterisk indicates a SphI site that is present in the 3′ end of the Sα2 locus, but not in the Sα1 locus. B, Genomic DNA from placenta (upper gel) and unstimulated CL-01 cells (bottom gel) was digested with BglII, HindIII, and SphI restriction enzymes; subjected to electrophoresis on a 0.7% agarose gel; blotted; and probed sequentially with the various σμ, Sμ, σδ, Sγ, Sα, and Sε region probes (shown above each lane).






References
-
- MacLennan IC. Germinal centers. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:117. - PubMed
-
- Liu YL, Malisan F, de Bouteiller O, Guret C, Lebecque S, Banchereau J, Mills FC, Max EE, Martinez-Valdez H. Within germinal centers, isotype switching of immunoglobulin genes occurs after the onset of somatic mutation. Immunity. 1996;4:241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
