Identification of a domain within the human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 envelope required for syncytium induction and replication
- PMID: 9499049
- PMCID: PMC109488
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.3.1959-1966.1998
Identification of a domain within the human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 envelope required for syncytium induction and replication
Erratum in
- J Virol 1998 Jul;72(7):6278
Abstract
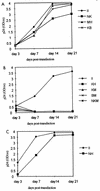
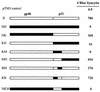
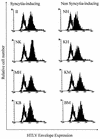
In vitro infection by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 and 2 (HTLV-1 and HTLV-2) can result in syncytium formation, facilitating viral entry. Using cell lines that were susceptible to HTLV-2-mediated syncytium formation but were nonfusogenic with HTLV-1, we constructed chimeric envelopes between HTLV-1 and -2 and assayed for the ability to induce syncytia in BJAB cells and HeLa cells. We have identified a fusion domain composed of the first 64 amino acids at the amino terminus of the HTLV-2 transmembrane protein, p21, the retention of which was required for syncytium induction. Construction of replication-competent HTLV genomic clones allowed us to correlate the ability of HTLV-2 to induce syncytia with the ability to replicate in BJAB cells. Differences in the ability to induce syncytia were not due to differences in the levels of total or cell membrane-associated envelope or in the formation of multimers. Therefore, we have localized a fusion domain within the amino terminus of the transmembrane protein of HTLV-2 envelope that is necessary for syncytium induction and viral replication.
Figures

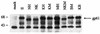

Similar articles
-
Analysis of functional conservation in the surface and transmembrane glycoprotein subunits of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-2.J Virol. 1998 Sep;72(9):7609-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.9.7609-7614.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9696862 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 receptor expression among syncytium-resistant cell lines revealed by a novel surface glycoprotein-immunoadhesin.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(17):8317-28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.17.8317-8328.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11483777 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning, expression, and biological characterization of an HTLV-II envelope glycoprotein: HIV-1 expression is permissive for HTLV-II-induced cell fusion.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Sep;9(9):849-60. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.849. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993. PMID: 8257634
-
Molecular mechanisms affecting HTLV type 1-dependent fusion at the cell membrane: implications for inhibiting viral transmission.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Nov 1;16(16):1731-6. doi: 10.1089/08892220050193227. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 11080818 Review.
-
Delineation of immunodominant epitopes of human T-lymphotropic virus types I and II and their usefulness in developing serologic assays for detection of antibodies to HTLV-I and HTLV-II.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1996;13 Suppl 1:S170-8. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199600001-00026. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1996. PMID: 8797720 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of functional conservation in the surface and transmembrane glycoprotein subunits of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-2.J Virol. 1998 Sep;72(9):7609-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.9.7609-7614.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9696862 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 receptor expression among syncytium-resistant cell lines revealed by a novel surface glycoprotein-immunoadhesin.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(17):8317-28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.17.8317-8328.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11483777 Free PMC article.
-
Envelope is a major viral determinant of the distinct in vitro cellular transformation tropism of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-2.J Virol. 2005 Dec;79(23):14536-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.23.14536-14545.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16282453 Free PMC article.
-
Highly specific inhibition of leukaemia virus membrane fusion by interaction of peptide antagonists with a conserved region of the coiled coil of envelope.Retrovirology. 2008 Aug 4;5:70. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-70. Retrovirology. 2008. PMID: 18680566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

