Adenovirus endocytosis via alpha(v) integrins requires phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase
- PMID: 9499060
- PMCID: PMC109499
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.3.2055-2061.1998
Adenovirus endocytosis via alpha(v) integrins requires phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase
Abstract
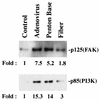
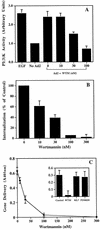
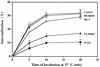
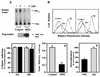
Integrins mediate cell adhesion and motility on the extracellular matrix, yet they also promote viral attachment and/or entry. Evidence is presented that adenovirus internalization by alpha(v) integrins requires activation of phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase (PI3K), whereas alpha(v) integrin-mediated cell motility depends on the ERK1/ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Interaction of adenovirus with alpha(v), integrins induced activation of PI3K. Pharmacologic or genetic disruption of endogenous PI3K activity blocked adenovirus internalization and virus-mediated gene delivery yet had no effect on integrin-mediated cell adhesion or motility. Therefore, integrin ligation engages distinct signaling pathways that promote viral endocytosis or cell movement.
Figures


References
-
- Carpenter C L, Cantley L C. Phosphoinositide kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:153–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

