Bovine papillomavirus type 1 genomes and the E2 transactivator protein are closely associated with mitotic chromatin
- PMID: 9499063
- PMCID: PMC109502
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.3.2079-2088.1998
Bovine papillomavirus type 1 genomes and the E2 transactivator protein are closely associated with mitotic chromatin
Abstract
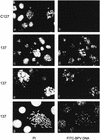
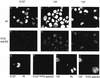
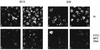
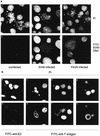
The bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 transactivator protein is required for viral transcriptional regulation and DNA replication and may be important for long-term episomal maintenance of viral genomes within replicating cells (M. Piirsoo, E. Ustav, T. Mandel, A. Stenlund, and M. Ustav, EMBO J. 15:1-11, 1996). We have evidence that, in contrast to most other transcriptional transactivators, the E2 transactivator protein is associated with mitotic chromosomes in dividing cells. The shorter E2-TR and E8/E2 repressor proteins do not bind to mitotic chromatin, and the N-terminal transactivation domain of the E2 protein is necessary for the association. However, the DNA binding function of E2 is not required. We have found that bovine papillomavirus type 1 genomes are also associated with mitotic chromosomes, and we propose a model in which E2-bound viral genomes are transiently associated with cellular chromosomes during mitosis to ensure that viral genomes are segregated to daughter cells in approximately equal numbers.
Figures





References
-
- Adom J N, Gouilleux F, Richard-Foy H. Interaction with the nuclear matrix of a chimeric construct containing a replication origin and a transcription unit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992;1171:187–197. - PubMed
-
- Adom J N, Richard-Foy H. A region immediately adjacent to the origin of replication of bovine papilloma virus type 1 interacts in vitro with the nuclear matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;176:479–485. - PubMed
-
- Bochkarev A, Barwell J A, Pfuetzner R A, Furey W J, Edwards A M, Frappier L. Crystal structure of the DNA-binding domain of the Epstein-Barr virus origin-binding protein EBNA 1. Cell. 1995;83:39–46. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

