Modulation of activity of Moloney murine leukemia virus preintegration complexes by host factors in vitro
- PMID: 9499068
- PMCID: PMC109507
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.3.2125-2131.1998
Modulation of activity of Moloney murine leukemia virus preintegration complexes by host factors in vitro
Abstract
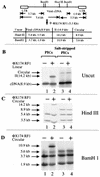
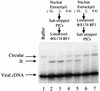
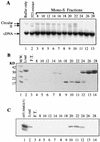
We have explored the requirements for host proteins in the integration of Moloney murine leukemia virus (MoMuLV) cDNA in vitro. Following infection, it is possible to lyse cells and obtain preintegration complexes (PICs) capable of integrating the MoMuLV cDNA into an added target DNA in vitro (intermolecular integration). PICs can be stripped of required proteins by gel filtration in high-salt buffers (600 mM KCI), allowing the nature of the removed factors to be investigated by in vitro reconstitution. In a previous study of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) PICs, the host protein HMG I(Y) was found to be able to restore activity to salt-stripped PICs. In contrast, salt stripping and reconstitution of MoMuLV PICs led to the proposal that a host factor is important for a different activity, blocking integration into the cDNA itself (autointegration). In this report, we investigated reconstitution of salt-stripped MoMuLV PICs and found that addition of cellular extract from uninfected NIH 3T3 cells could block autointegration and also restore intermolecular integration. Isolation of the intermolecular integration-complementing activity yielded HMG I(Y), as in the HIV-1 case. However, HMG I(Y) could not block autointegration, implicating a different host factor in this process. Additionally, when MoMuLV PICs were partially purified but not salt stripped, the intermolecular integration activity was reduced but could be stimulated by the addition of any of several purified DNA binding proteins. In summary, three activities were detected: (i) the intermolecular integration cofactor HMG I(Y), (ii) an autointegration barrier protein, and (iii) stimulatory DNA binding proteins.
Figures

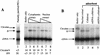
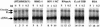
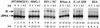
Similar articles
-
Retroviral cDNA integration: stimulation by HMG I family proteins.J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):10965-74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.23.10965-10974.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11069991 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory mechanisms by which barrier-to-autointegration factor blocks autointegration and stimulates intermolecular integration of Moloney murine leukemia virus preintegration complexes.J Virol. 2002 Dec;76(23):12376-80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.23.12376-12380.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12414981 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 cDNA integration: requirement of HMG I(Y) protein for function of preintegration complexes in vitro.Cell. 1997 Feb 21;88(4):483-92. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81888-7. Cell. 1997. PMID: 9038339
-
Cellular co-factors of HIV-1 integration.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Feb;31(2):98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2005.12.002. Epub 2006 Jan 5. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16403635 Review.
-
Minor groove-binding architectural proteins: structure, function, and DNA recognition.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998;27:105-31. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.27.1.105. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998. PMID: 9646864 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transduction of nondividing human macrophages with gammaretrovirus-derived vectors.J Virol. 2006 Feb;80(3):1152-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.3.1152-1159.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16414992 Free PMC article.
-
Retroviral cDNA integration: stimulation by HMG I family proteins.J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):10965-74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.23.10965-10974.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11069991 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory mechanisms by which barrier-to-autointegration factor blocks autointegration and stimulates intermolecular integration of Moloney murine leukemia virus preintegration complexes.J Virol. 2002 Dec;76(23):12376-80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.23.12376-12380.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12414981 Free PMC article.
-
Cofactors for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 cDNA integration in vitro.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(2):1598-603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.2.1598-1603.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12502875 Free PMC article.
-
Many nonmammalian cells exhibit postentry blocks to transduction by gammaretroviruses pseudotyped with various viral envelopes, including vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein.J Virol. 2001 Jul;75(14):6375-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.14.6375-6383.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11413304 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

