Cytosolic Gag p24 as an index of productive entry of human immunodeficiency virus type 1
- PMID: 9499078
- PMCID: PMC109517
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.3.2208-2212.1998
Cytosolic Gag p24 as an index of productive entry of human immunodeficiency virus type 1
Abstract
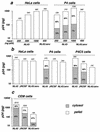
We have investigated the cellular uptake of Gag p24 shortly after exposure of cells to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) particles. In the absence of envelope glycoprotein on virions or of viral receptors or coreceptors at the cell surface, p24 was incorporated in intracellular vesicles but not detected in the cytosolic subcellular fraction. When appropriate envelope-receptor interactions could occur, the nonspecific vesicular uptake was still intense and cytosolic p24 represented 10 to 40% of total intracellular p24. The measurement of cytosolic p24 early after exposure to HIV type 1 is a reliable assay for investigating virus entry and early events leading to authentic cell infection.
Figures

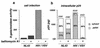
References
-
- Amara A, Le Gall S, Schwartz O, Salamero J, Montes M, Loetscher P, Baggioloni M, Virelizier J L, Arenzana-Seisdedos F. HIV co-receptor down-regulation as anti-viral principle. SDF-1a dependent internalization of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 contributes to inhibition of HIV replication. J Exp Med. 1997;186:139–146. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Charneau P, Mirabeau G, Roux P, Paulous S, Buc H, Clavel F. HIV-1 reverse transcription: a termination step at the center of the genome. J Mol Biol. 1994;241:651–662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

