Enhanced virus clearance by early inducible lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-neutralizing antibodies in immunoglobulin-transgenic mice
- PMID: 9499083
- PMCID: PMC109522
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.3.2253-2258.1998
Enhanced virus clearance by early inducible lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-neutralizing antibodies in immunoglobulin-transgenic mice
Abstract
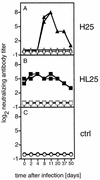
Following infection of mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), virus-neutralizing antibodies appear late, after 30 to 60 days. Such neutralizing antibodies play an important role in protection against reinfection. To analyze whether a neutralizing antibody response which developed earlier could contribute to LCMV clearance during the acute phase of infection, we generated transgenic mice expressing LCMV-neutralizing antibodies. Transgenic mice expressing the immunoglobulin mu heavy chain of the LCMV-neutralizing monoclonal antibody KL25 (H25 transgenic mice) mounted LCMV-neutralizing immunoglobulin M (IgM) serum titers within 8 days after infection. This early inducible LCMV-neutralizing antibody response significantly improved the host's capacity to clear the infection and did not cause an enhancement of disease after intracerebral (i.c.) LCMV infection. In contrast, mice which had been passively administered LCMV-neutralizing antibodies and transgenic mice exhibiting spontaneous LCMV-neutralizing IgM serum titers (HL25 transgenic mice expressing the immunoglobulin mu heavy and the kappa light chain) showed an enhancement of disease after i.c. LCMV infection. Thus, early-inducible LCMV-neutralizing antibodies can contribute to viral clearance in the acute phase of the infection and do not cause antibody-dependent enhancement of disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vivo selection of neutralization-resistant virus variants but no evidence of B cell tolerance in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus carrier mice expressing a transgenic virus-neutralizing antibody.J Immunol. 1999 Apr 15;162(8):4536-41. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10201992
-
Antiviral immune responses in gene-targeted mice expressing the immunoglobulin heavy chain of virus-neutralizing antibodies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12883-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2135542100. Epub 2003 Oct 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14569006 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-specific MHC-class II-restricted TCR-transgenic mice: effects on humoral and cellular immune responses after viral infection.Eur J Immunol. 1998 Jan;28(1):390-400. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199801)28:01<390::AID-IMMU390>3.0.CO;2-O. Eur J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9485218
-
Viral escape from the neutralizing antibody response: the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus model.Immunogenetics. 2001 Apr;53(3):185-9. doi: 10.1007/s002510100314. Immunogenetics. 2001. PMID: 11398962 Review.
-
Public, private and non-specific antibodies induced by non-cytopathic viral infections.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004 Aug;7(4):426-33. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.06.008. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15358263 Review.
Cited by
-
Interrogating Adaptive Immunity Using LCMV.Curr Protoc Immunol. 2020 Sep;130(1):e99. doi: 10.1002/cpim.99. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32940427 Free PMC article.
-
Early antibodies specific for the neutralizing epitope on the receptor binding subunit of the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus glycoprotein fail to neutralize the virus.J Virol. 2007 Nov;81(21):11650-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00955-07. Epub 2007 Aug 15. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17699567 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of protective antibodies are determined by the viral surface antigen.J Clin Invest. 2004 Oct;114(7):988-93. doi: 10.1172/JCI22374. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15467838 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired antibody response causes persistence of prototypic T cell-contained virus.PLoS Biol. 2009 Apr 7;7(4):e1000080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000080. PLoS Biol. 2009. PMID: 19355789 Free PMC article.
-
The adaptor molecule CD2AP in CD4 T cells modulates differentiation of follicular helper T cells during chronic LCMV infection.PLoS Pathog. 2018 May 7;14(5):e1007053. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007053. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29734372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberti A, Pontisso P, Tagariello G, Cavalletto D, Chemello L, Belussi F. Antibody response to pre-S2 and hepatitis B virus induced liver damage. Lancet. 1988;25:1421–1424. - PubMed
-
- Andersson B, Skoglund A C, Ronnholm M, Lindsten T, Lamon E W, Collisson E W, Walia A S. Functional aspects of IgM and IgG Fc receptors on murine T lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1981;56:5–50. - PubMed
-
- Baer G M, Bellini W J, Fishbein D B. Rhabdoviruses. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, editors. Virology. New York, N.Y: Raven Press; 1990. pp. 883–930.
-
- Battegay M, Cooper S, Althage A, Baenziger J, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel R M. Quantification of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus with an immunological focus assay in 24 or 96 well plates. J Virol Methods. 1991;33:191–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

