Eph receptors discriminate specific ligand oligomers to determine alternative signaling complexes, attachment, and assembly responses
- PMID: 9499402
- PMCID: PMC316584
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.5.667
Eph receptors discriminate specific ligand oligomers to determine alternative signaling complexes, attachment, and assembly responses
Abstract
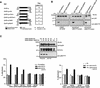
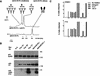
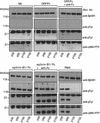
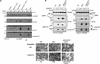
Eph family receptor tyrosine kinases (including EphA3, EphB4) direct pathfinding of neurons within migratory fields of cells expressing gradients of their membrane-bound ligands. Others (EphB1 and EphA2) direct vascular network assembly, affecting endothelial migration, capillary morphogenesis, and angiogenesis. To explore how ephrins could provide positional labels for cell targeting, we tested whether endogenous endothelial and P19 cell EphB1 (ELK) and EphB2 (Nuk) receptors discriminate between different oligomeric forms of an ephrin-B1/Fc fusion ligand. Receptor tyrosine phosphorylation was stimulated by both dimeric and clustered multimeric ephrin-B1, yet only ephrin-B1 multimers (tetramers) promoted endothelial capillary-like assembly, cell attachment, and the recruitment of low-molecular-weight phosphotyrosine phosphatase (LMW-PTP) to receptor complexes. Cell-cell contact among cells expressing both EphB1 and ephrin-B1 was required for EphB1 activation and recruitment of LMW-PTP to EphB1 complexes. The EphB1-binding site for LMW-PTP was mapped and shown to be required for tetrameric ephrin-B1 to recruit LMW-PTP and to promote attachment. Thus, distinct EphB1-signaling complexes are assembled and different cellular attachment responses are determined by a receptor switch mechanism responsive to distinct ephrin-B1 oligomers.
Figures



References
-
- Bain G, Ray WJ, Yao M, Gottlieb DI. From embryonal carcinoma cells to neurons: The P19 pathway. BioEssays. 1994;15:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Bohme B, VandenBos T, Cerretti DP, Park LS, Hotrich U, Ruebsamen-Waigmann H, Strebhardt K. Cell-cell adhesion mediated by binding of membrane-anchored ligand LERK-2 to the EPH-related receptor human embryonal kinase 2 promotes tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:24747–24752. - PubMed
-
- Brambilla R, Brueckner K, Orioli D, Bergemann AD, Flanagan JG, Klein R. Similarities and differences in the way transmembrane-type ligands interact with the ELK subclass of Eph receptors. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;8:199–209. - PubMed
-
- Brennan C, Monschau B, Lindberg R, Guthrie B, Drescher U, Bonhoeffer F, Holder N. Two Eph receptor tyrosine kinase ligands control axon growth and may be involved in the creation of the retinotectal map in the zebrafish. Development. 1997;124:655–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
