The essential mitotic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 binds and regulates mitosis-specific phosphoproteins
- PMID: 9499405
- PMCID: PMC316589
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.5.706
The essential mitotic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 binds and regulates mitosis-specific phosphoproteins
Abstract
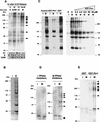
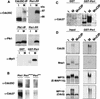
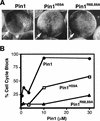
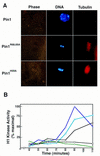
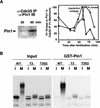
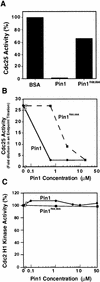
Phosphorylation of mitotic proteins on the Ser/Thr-Pro motifs has been shown to play an important role in regulating mitotic progression. Pin1 is a novel essential peptidyl-prolyl isomerase (PPIase) that inhibits entry into mitosis and is also required for proper progression through mitosis, but its substrate(s) and function(s) remain to be determined. Here we report that in both human cells and Xenopus extracts, Pin1 interacts directly with a subset of mitotic phosphoproteins on phosphorylated Ser/Thr-Pro motifs in a phosphorylation-dependent and mitosis-specific manner. Many of these Pin1-binding proteins are also recognized by the monoclonal antibody MPM-2, and they include the important mitotic regulators Cdc25, Myt1, Wee1, Plk1, and Cdc27. The importance of this Pin1 interaction was tested by constructing two Pin1 active site point mutants that fail to bind a phosphorylated Ser/Thr-Pro motif in mitotic phosphoproteins. Wild-type, but not mutant, Pin1 inhibits both mitotic division in Xenopus embryos and entry into mitosis in Xenopus extracts. We have examined the interaction between Pin1 and Cdc25 in detail. Pin1 not only binds the mitotic form of Cdc25 on the phosphorylation sites important for its activity in vitro and in vivo, but it also inhibits its activity, offering one explanation for the ability of Pin1 to inhibit mitotic entry. In a separate paper, we have shown that Pin1 is a phosphorylation-dependent PPIase that can recognize specifically the phosphorylated Ser/Thr-Pro bonds present in mitotic phosphoproteins. Thus, Pin1 likely acts as a general regulator of mitotic proteins that have been phosphorylated by Cdc2 and other mitotic kinases.
Figures

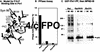
Similar articles
-
The mitotic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase, Pin1, interacts with Cdc25 and Plx1.EMBO J. 1998 Aug 10;17(5):1315-27. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.5.1315. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9482729 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-dependent prolyl isomerization: a novel signaling regulatory mechanism.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 Nov 30;56(9-10):788-806. doi: 10.1007/s000180050026. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999. PMID: 11212339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequence-specific and phosphorylation-dependent proline isomerization: a potential mitotic regulatory mechanism.Science. 1997 Dec 12;278(5345):1957-60. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5345.1957. Science. 1997. PMID: 9395400
-
Requirement of the prolyl isomerase Pin1 for the replication checkpoint.Science. 2000 Mar 3;287(5458):1644-7. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5458.1644. Science. 2000. PMID: 10698738
-
The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003;5:477-87. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003. PMID: 14593743 Review.
Cited by
-
Pin1 inhibits PP2A-mediated Rb dephosphorylation in regulation of cell cycle and S-phase DNA damage.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Feb 12;6(2):e1640. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.3. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25675300 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of MEF2C contributes to regulate G2/M transition.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(10):1517-28. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1026519. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25789873 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways that control mRNA turnover.Cell Signal. 2013 Aug;25(8):1699-710. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.03.026. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23602935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
It's all about tau.Prog Neurobiol. 2019 Apr;175:54-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2018.12.005. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Prog Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30605723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pin1 is overexpressed in breast cancer and cooperates with Ras signaling in increasing the transcriptional activity of c-Jun towards cyclin D1.EMBO J. 2001 Jul 2;20(13):3459-72. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.13.3459. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11432833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailly E, McCaffrey M, Touchot N, Zahraoui A, Goud B, Bornens M. Phosphorylation of two small GTP-binding proteins of the Rab family by p34cdc2. Nature. 1991;350:715–718. - PubMed
-
- Blangy A, Lane HA, d’Herin P, Harper M, Kress M, Nigg EA. Phosphorylation by p34cdc2 regulates spindle association of human Eg5, a kinesin-related motor essential for bipolar spindle formation in vivo. Cell. 1995;83:1159–1169. - PubMed
-
- Booher RN, Holman PS, Fattaey A. Human Myt1 is a cell cycle-regulated kinase that inhibits Cdc2 but not Cdk2 activity. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:22300–22306. - PubMed
-
- Coleman TR, Dunphy WG. Cdc2 regulatory factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:877–882. - PubMed
-
- Coleman TR, Tang Z, Dunphy WG. Negative regulation of the wee1 protein kinase by direct action of the nim1/cdr1 mitotic inducer. Cell. 1993;72:919–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
