Differential colocalization of estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) with oxytocin and vasopressin in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the female rat brain: an immunocytochemical study
- PMID: 9501254
- PMCID: PMC19733
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3281
Differential colocalization of estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) with oxytocin and vasopressin in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the female rat brain: an immunocytochemical study
Abstract
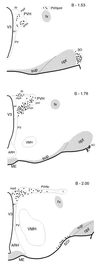
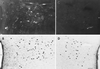
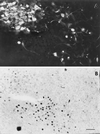
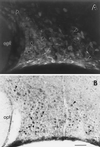
Evidence exists for the localization of the newly identified estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) within the rat paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and supraoptic nucleus (SON), regions which lack ERalpha. Presently, we investigate whether ERbeta-like-immunoreactivity (-ir) is found within cells of several major neuropeptide systems of these regions. Young adult Sprague-Dawley rats were ovariectomized (OVX), and 1 week later half of the animals received estradiol-17beta (E). Dual-label immunocytochemistry was performed on adjacent sections by using an ERbeta antibody, followed by an antibody to either oxytocin (OT), arginine-vasopressin (AVP), or corticotropin releasing hormone. Nuclear ERbeta-ir was identified within SON and retrochiasmatic SON, and in specific PVN subnuclei: medial parvicellular part, ventral and dorsal zones, dorsal and lateral parvicellular parts, and in the posterior magnocellular part, medial and lateral zones. However, the ERbeta-ir within magnocellular areas was noticeably less intense. OT-/ERbeta-ir colocalization was confirmed in neurons of the parvicellular subnuclei, in both OVX and OVX+E brains ( approximately 50% of OT and 25% of ERbeta-labeled cells between bregma -1.78 and -2.00). In contrast, few PVN parvicellular neurons contained both AVP- and ERbeta-ir. As well, very little overlap was observed in the distribution of cells containing corticotropin releasing hormone- or ERbeta-ir. In the SON, most nuclear ERbeta-ir colocalized with AVP-ir, whereas few OT-/ERbeta-ir dual-labeled cells were observed. These findings suggest that estrogen can directly modulate specific OT and AVP systems through an ERbeta-mediated mechanism, in a tissue-specific manner.
Figures
References
-
- Mosselman S, Polman J, Dijkema R. FEBS Lett. 1996;392:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Tremblay G B, Tremblay A, Copeland N G, Gilbert D J, Jenkins N, Labrie F, Giguere V. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:353–365. - PubMed
-
- Kuiper G G J M, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Haggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson J-A. Endocrinology. 1997;138:863–870. - PubMed
-
- Paech K, Webb P, Kuiper G G J M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson J-A, Kushner P, Scanlan T S. Science. 1997;277:1508–1510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

