Upregulation of L-type Ca2+ channels in reactive astrocytes after brain injury, hypomyelination, and ischemia
- PMID: 9502793
- PMCID: PMC6793103
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-07-02321.1998
Upregulation of L-type Ca2+ channels in reactive astrocytes after brain injury, hypomyelination, and ischemia
Abstract
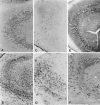
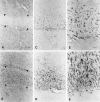
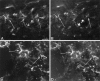
Anti-peptide antibodies that specifically recognize the alpha1 subunit of class A-D voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and a monoclonal antibody (MANC-1) to the alpha2 subunit of L-type Ca2+ channels were used to investigate the distribution of these Ca2+ channel subtypes in neurons and glia in models of brain injury, including kainic acid-induced epilepsy in the hippocampus, mechanical and thermal lesions in the forebrain, hypomyelination in white matter, and ischemia. Immunostaining of the alpha2 subunit of L-type Ca2+ channels by the MANC-1 antibody was increased in reactive astrocytes in each of these forms of brain injury. The alpha1C subunits of class C L-type Ca2+ channels were upregulated in reactive astrocytes located in the affected regions in each of these models of brain injury, although staining for the alpha1 subunits of class D L-type, class A P/Q-type, and class B N-type Ca2+ channels did not change from patterns normally observed in control animals. In all of these models of brain injury, there was no apparent redistribution or upregulation of the voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in neurons. The upregulation of L-type Ca2+ channels in reactive astrocytes may contribute to the maintenance of ionic homeostasis in injured brain regions, enhance the release of neurotrophic agents to promote neuronal survival and differentiation, and/or enhance signaling in astrocytic networks in response to injury.
Figures






References
-
- Ahlijanian MK, Westenbroek RE, Catterall WA. Subunit structure and localization of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels in mammalian brain, spinal cord, and retina. Neuron. 1990;4:819–832. - PubMed
-
- Aicardi G, Schwartzkroin PA. Suppression of epileptiform burst discharges in CA1 neurons of rat hippocampal slices by the organic Ca2+ channel blocker, verapamil. Exp Brain Res. 1990;81:288–296. - PubMed
-
- Andersson H, Luthman J, Oslon L. Trimethyltin-induced expression of GABA and vimentin immunoreactivities in astrocytes of the rat brain. Glia. 1994;11:378–382. - PubMed
-
- Astrup J, Norberg K. K+ activity in cerebral cortex in rats during progressive severe hypoglycemia. Brain Res. 1976;103:418–423. - PubMed
-
- Ballarin M, Ernfors P, Linderfors N, Persson H. Hippocampal damage and kainic acid injection induce a rapid increase in mRNA for BDNF and NGF in the rat brain. Exp Neurol. 1991;114:35–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
