Reduction of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine-modified assembly protein-3 in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 9502801
- PMCID: PMC6793091
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-07-02399.1998
Reduction of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine-modified assembly protein-3 in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
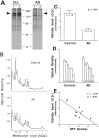
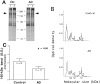
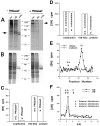
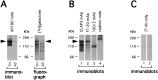
Abnormal protein processing and modification is associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. The role of phosphorylation in AD has been studied extensively because the presumed abnormal phosphorylation of tau protein is believed to play a role in the formation of paired helical filaments. Glycosylation with O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) to serine and threonine residues is a dynamic protein modification of intracellular proteins, and it shares similar features with protein phosphorylation. In this study, O-GlcNAc glycosylation of proteins from autopsied human brains with confirmed AD and non-AD age-matched controls was examined. O-GlcNAcylation was demonstrated by labeling protein extracts with [3H]galactose in the presence of galactosyltransferase and subsequent analyses of saccharide-protein linkage and saccharide structure. The number of O-GlcNAc-containing proteins and the overall O-GlcNAc level do not appear to be different between AD and control brain tissues. The only significant change observed is a marked reduction of O-GlcNAcylated clathrin assembly protein-3 (AP-3) in AD. The reduction is more evident in brain neocortical regions, and there appears to be a negative correlation between O-glycosylated AP-3 and the density of neurofibrillary tangles. These data suggest a possible association between the O-glycosylated AP-3 and AD pathology.
Figures





References
-
- Alzheimer A. Uber eine eigenartige Erkrangkung der Himrinde. All Z Psychiatr. 1907;64:146–148.
-
- Arnold CS, Johnson GVW, Cole RN, Dong DLY, Lee M, Hart GW. The microtubule-associated protein tau is extensively modified with O-linked N-acetylglucosamine. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:28741–28744. - PubMed
-
- Arriagada PV, Growdon JH, Hedley-Whyte T, Hyman BT. Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1992;42:631–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
