Glycinergic synaptic inputs to bipolar cells in the salamander retina
- PMID: 9503334
- PMCID: PMC2230757
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.731bv.x
Glycinergic synaptic inputs to bipolar cells in the salamander retina
Abstract
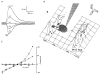
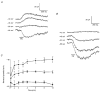
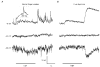
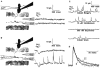
1. Glycine activated strychnine-sensitive chloride conductances at both the dendrites and the axonal telodendria of most bipolar cells in the salamander retina. 2. The chloride equilibrium potential of bipolar cells was found to be negative to -50 mV, indicating that glycinergic synapses on bipolar cells are inhibitory. 3. Some bipolar cells exhibited discrete, strychnine-sensitive, chloride-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs). These were elicited by focal application of glutamate at the inner plexiform layer (IPL). Glycinergic synapses were localized using simultaneous focal application of calcium to retinal slices bathed in calcium-free media. Both dendritic and telodendritic glycinergic IPSCs were observed. 4. The decay of the telodendritic IPSCs was well fitted by a single exponential with a time constant of 17.7 +/- 8.7 ms. Similar kinetics were observed for dendritic IPSCs in some cells, but in one class of on-centre bipolar cell the decay of the dendritic IPSCs was better fitted by a sum of two exponentials with time constants 9.9 +/- 4.3 and 51.3 +/- 24.3 ms. 5. The dendritic IPSCs were best driven by application of glutamate at the distal IPL (the off sublamina), while the telodendritic IPSCs were driven best by application near the telodendria. These results suggest that bipolar cell dendrites receive inhibitory glycinergic inputs from interplexiform cells that are excited by off-centre bipolar cells, whereas bipolar cell telodendria receive glycinergic amacrine cell inputs that are antagonistic to the photoreceptor inputs. 6. Both inputs could be elicited in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX), but the dendritic IPSCs were sometimes abolished by TTX, suggesting that sodium-dependent spikes play an important role in the transmission of interplexiform cell signals to the outer plexiform layer.
Figures


References
-
- Famiglietti EV, Jr, Kaneko A, Tachibana M. Neuronal architecture of on and off pathways to ganglion cells in carp retina. Science. 1977;198:1267–1269. - PubMed
-
- Famiglietti EV, Jr, Kolb H. Structural basis for ON-and OFF-center responses in retinal ganglion cells. Science. 1976;194:193–195. - PubMed
-
- Gao F, Yang J-H, Wu SM. Miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents in retinal ganglion cells. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. 1997;38:S51. abstract 242.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

