Expression of a marker for colonic crypt base cells is correlated with poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer
- PMID: 9505887
- PMCID: PMC1726940
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.42.1.63
Expression of a marker for colonic crypt base cells is correlated with poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: There is a need for markers in colorectal cancer which will allow subclassification of stage groups into subgroups with high versus low risk of recurrent disease.
Aims: To develop monoclonal antibodies that recognise antigens or immature crypt base cells, on the assumption that in a neoplasm undifferentiated but not the terminally differentiated cells will be responsible for tumour progression.
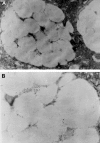
Methods: Colon crypt cells which were isolated from human colonic mucosa by EDTA/EGTA incubation were studied. By stepwise harvesting, crypt base cell enriched fractions were obtained, and after incubation with antibodies against dominant antigens, used as immunogens.
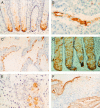
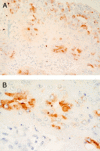
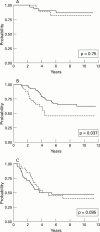
Results: Of one crypt base cell specific antibody (5E9), the reactive epitope appeared to be a non-terminal carbohydrate in the mucin O-glycans of the colon. The epitope did not seem to be colon specific, but was expressed in a variety of other tissues. In colorectal carcinomas, 5E9 immunoreactivity identified a subgroup of patients with a tendency for worse prognosis.
Conclusion: A mucin associated maturation epitope was identified in colonic crypt base cells, the expression of which in Dukes' stage B3 colorectal carcinoma may be associated with poor prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human colon adenocarcinomas express a MUC1-associated novel carbohydrate epitope on core mucin glycans defined by a monoclonal antibody (A10) raised against murine Ehrlich tumor cells.Cancer Res. 1999 Mar 1;59(5):1061-70. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10070964
-
A novel gastric-cancer-associated mucin antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody A3D4.Int J Cancer. 1997 Dec 10;73(6):795-801. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19971210)73:6<795::aid-ijc4>3.0.co;2-y. Int J Cancer. 1997. PMID: 9399654
-
Oncofetal mucin M1 epitope family: characterization and expression during colonic carcinogenesis.Int J Cancer. 1991 Jan 21;47(2):304-10. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470222. Int J Cancer. 1991. PMID: 1988372
-
[Mucin-associated antigens as markers of gastrointestinal differentiation and carcinogenesis].Pathologe. 1995 Mar;16(2):94-105. doi: 10.1007/s002920050082. Pathologe. 1995. PMID: 7539132 Review. German.
-
Host response in tumor diagnosis and prognosis: importance of immunologists and pathologists alliance.Exp Mol Pathol. 2012 Dec;93(3):315-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 23099314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
