Detection of intimins alpha, beta, gamma, and delta, four intimin derivatives expressed by attaching and effacing microbial pathogens
- PMID: 9508292
- PMCID: PMC104605
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.3.662-668.1998
Detection of intimins alpha, beta, gamma, and delta, four intimin derivatives expressed by attaching and effacing microbial pathogens
Abstract
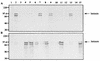
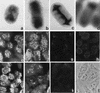
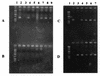
Intimins are outer membrane proteins expressed by enteric bacterial pathogens capable of inducing intestinal attachment-and-effacement lesions. A eukaryotic cell-binding domain is located within a 280-amino-acid (Int280) carboxy terminus of intimin polypeptides. Polyclonal antiserum was raised against Int280 from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) serotypes O127:H6 and O114:H2 (anti-Int280-H6 and anti-Int280-H2, respectively), and Western blot analysis was used to explore the immunological relationship between the intimin polypeptides expressed by different clinical EPEC and enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) isolates, a rabbit diarrheagenic E. coli strain (RDEC-1), and Citrobacter rodentium. Anti-Int280-H6 serum reacted strongly with some EPEC serotypes, whereas anti-Int280-H2 serum reacted strongly with strains belonging to different EPEC and EHEC serotypes, RDEC-1, and C. rodentium. These observations were confirmed by using purified Int280 in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and by immunogold and immunofluorescence labelling of whole bacterial cells. Some bacterial strains were recognized poorly by either antiserum (e.g., EPEC O86:H34 and EHEC O157:H7). By using PCR primers designed on the basis of the intimin-encoding eae gene sequences of serotype O127:H6, O114:H2, and O86:H34 EPEC and serotype O157:H7 EHEC, we could distinguish between different eae gene derivatives. Accordingly, the different intimin types were designated alpha, beta, delta, and gamma, respectively.
Figures
References
-
- Agin T S, Cantey J R, Boedeker E C, Wolf M K. Characterisation of the eae gene from rabbit enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 and comparison to other eae genes from bacteria that cause attaching and effacing lesions. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1996;144:249–258. - PubMed
-
- Albert M J, Faruque S M, Ansaruzzaman M, Islam M M, Haider K, Alam K, Kabir I, Robins-Browne R. Sharing of virulence-associated properties at the phenotypic and genetic levels between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Hafnia alvei. J Med Microbiol. 1992;37:310–314. - PubMed
-
- Barthold S W, Coleman G L, Bhatt P N, Osbaldiston G W, Jones A M. The etiology of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Lab Anim Sci. 1976;26:889–894. - PubMed
-
- Beebakhee G, Louie M, De Azavedo J, Brunton J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the eae gene homologue from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992;70:63–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

