Replicon clusters are stable units of chromosome structure: evidence that nuclear organization contributes to the efficient activation and propagation of S phase in human cells
- PMID: 9508763
- PMCID: PMC2132671
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.140.6.1285
Replicon clusters are stable units of chromosome structure: evidence that nuclear organization contributes to the efficient activation and propagation of S phase in human cells
Abstract
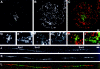
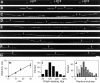
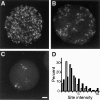
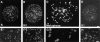
In proliferating cells, DNA synthesis must be performed with extreme precision. We show that groups of replicons, labeled together as replicon clusters, form stable units of chromosome structure. HeLa cells were labeled with 5-bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) at different times of S phase. At the onset of S phase, clusters of replicons were activated in each of approximately 750 replication sites. The majority of these replication "foci" were shown to be individual replicon clusters that remained together, as stable cohorts, throughout the following 15 cell cycles. In individual cells, the same replication foci were labeled with BrdU and 5-iododeoxyuridine at the beginning of different cell cycles. In DNA fibers, 95% of replicons in replicon clusters that were labeled at the beginning of one S phase were also labeled at the beginning of the next. This shows that a subset of origins are activated both reliably and efficiently in different cycles. The majority of replication forks activated at the onset of S phase terminated 45-60 min later. During this interval, secondary replicon clusters became active. However, while the activation of early replicons is synchronized at the onset of S phase, different secondary clusters were activated at different times. Nevertheless, replication foci pulse labeled during any short interval of S phase were stable for many cell cycles. We propose that the coordinated replication of related groups of replicons, that form stable replicon clusters, contributes to the efficient activation and propagation of S phase in mammalian cells.
Figures



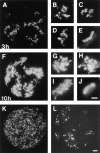
References
-
- Baumgartner M, Dutrillaux B, Lemieux N, Paulin D, Viegas-Pequignot E. Genes occupy a fixed and symmetrical position on sister chromatids. Cell. 1991;64:761–767. - PubMed
-
- Berezney R, Mortillaro MJ, Ma H, Wei X, Samarabandu J. The nuclear matrix: a structural milieu for genomic function. Int Rev Cytol. 1995a;162:1–65. - PubMed
-
- Berezney R, Ma H, Meng C, Samarabandu J, Cheng PC. Connecting genomic architecture and DNA replication in three dimensions. Zool Studies. 1995b;1(Suppl.):29–32.
-
- Cocker JH, Piatti S, Santocanale C, Nasmyth K, Diffley JFX. An essential role for the Cdc6 protein in forming the pre-replicative complexes of budding yeast. Nature. 1996;379:180–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

