A requirement for cyclin D3-cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk)-4 assembly in the cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent proliferation of thyrocytes
- PMID: 9508775
- PMCID: PMC2132659
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.140.6.1427
A requirement for cyclin D3-cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk)-4 assembly in the cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent proliferation of thyrocytes
Abstract
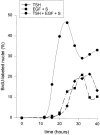
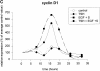
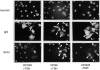
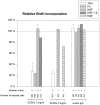
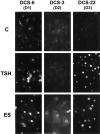
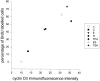
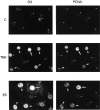
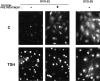
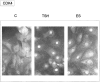
In different systems, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) either blocks or promotes cell cycle progression in mid to late G1 phase. Dog thyroid epithelial cells in primary culture constitute a model of positive control of DNA synthesis initiation and G0-S prereplicative phase progression by cAMP as a second messenger for thyrotropin (TSH). The cAMP-dependent mitogenic pathway is unique as it is independent of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and differs from growth factor-dependent pathways at the level of the expression of several protooncogenes/transcription factors. This study examined the involvement of D-type G1 cyclins and their associated cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk4) in the cAMP-dependent G1 phase progression of dog thyroid cells. Unlike epidermal growth factor (EGF)+serum and other cAMP-independent mitogens, TSH did not induce the accumulation of cyclins D1 and D2 and partially inhibited the basal expression of the most abundant cyclin D3. However, TSH stimulation enhanced the nuclear detection of cyclin D3. This effect correlated with G1 and S phase progression. It was found to reflect both the unmasking of an epitope of cyclin D3 close to its domain of interaction with cdk4, and the nuclear translocation of cyclin D3. TSH and EGF+serum also induced a previously undescribed nuclear translocation of cdk4, the assembly of precipitable cyclin D3-cdk4 complexes, and the Rb kinase activity of these complexes. Previously, cdk4 activity was found to be required in the cAMP-dependent mitogenic pathway of dog thyrocytes, as in growth factor pathways. Here, microinjections of a cyclin D3 antibody showed that cyclin D3 is essential in the TSH/ cAMP-dependent mitogenesis, but not in the pathway of growth factors that induce cyclins D1 and D2. The present study (a) provides the first example in a normal cell of a stimulation of G1 phase progression occurring independently of an enhanced accumulation of cyclins D, (b) identifies the activation of cyclin D3 and cdk4 through their enhanced assembly and/or nuclear translocation, as first convergence steps of the parallel cAMP-dependent and growth factor mitogenic pathways, and (c) strongly suggests that this new mechanism is essential in the cAMP-dependent mitogenesis, which provides the first direct demonstration of the requirement for cyclin D3 in a G1 phase progression.
Figures





References
-
- Ajchenbaum F, Ando K, De Caprio JA, Griffin JD. Independent regulation of human D-type cyclin gene expression during G1 phase in primary human T lymphocytes. J. Biol Chem. 1993;268:4113–4119. - PubMed
-
- Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcotte MJ, Pagano M, Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993;7:812–821. - PubMed
-
- Baptist M, Dumont JE, Roger PP. Demonstration of cell cycle kinetics in thyroid primary culture by immunostaining of proliferating cell nuclear antigen: differences in cyclic AMP-dependent and -independent mitogenic stimulations. J Cell Sci. 1993;105:69–80. - PubMed
-
- Baptist M, Dumont JE, Roger PP. Intercellular heterogeneity of early mitogenic events: cAMP generalizes the EGF effect on c-Fos protein appearance but not on MAP kinase phosphorylation and nuclear translocation in dog thyroid epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1995;221:160–171. - PubMed
-
- Baptist M, Lamy F, Gannon J, Hunt T, Dumont JE, Roger PP. Expression and subcellular localization of CDK2 and cdc2 kinases and their common partner cyclin A in thyroid epithelial cells: comparison of cyclic AMP-dependent and -independent cell cycles. J Cell Physiol. 1996;166:256–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

